3D comparison of low, intermediate, and advanced hippocampal atrophy in MCI
- PMID: 20143386
- PMCID: PMC2938765
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20905
3D comparison of low, intermediate, and advanced hippocampal atrophy in MCI
Erratum in
- Hum Brain Mapp. 2010 Dec;31(12):2015
Abstract
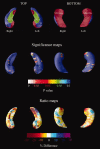
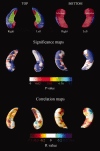
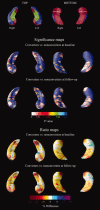
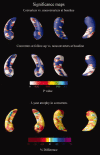
We applied the hippocampal radial atrophy mapping technique to the baseline and follow-up magnetic resonance image data of 169 amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) participants in the imaging arm of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study MCI Donepezil/Vitamin E trial. Sixty percent of the subjects with none to mild hippocampal atrophy rated with the visual medial temporal atrophy rating scale (MTA score < 2) and 33.8% of the subjects with moderate to severe (MTA > or = 2) hippocampal atrophy converted to Alzheimer's disease (AD) during 3-year follow-up. MTA > or = 2 showed a trend for greater left sided hippocampal atrophy versus MTA < 2 groups at baseline (P(corrected) = 0.08). Higher MTA scores were associated with progressive atrophy of the subiculum and the CA1-3 subregions. The MTA < 2 group demonstrated significant bilateral atrophy progression at follow-up (left P(corrected) = 0.008; right P(corrected) = 0.05). Relative to MTA < 2 nonconverters, MTA < 2 converters showed further involvement of the subiculum and CA1 and additional involvement of CA2-3 at follow-up. Right CA1 atrophy was significantly associated with conversion to dementia (for 1 mm greater right CA1 radial distance subjects had 50% reduced hazard for conversion). Greater CA1 and subicular atrophy can be demonstrated early and is predictive of future conversion to AD, whereas CA2-3 involvement becomes more evident as the disease progresses.
Figures

References
-
- Apostolova LG, Dinov ID, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM ( 2006a): 3D comparison of hippocampal atrophy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Brain 129 ( Pt 11): 2867–2873. - PubMed
-
- Apostolova LG, Dutton RA, Dinov ID, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM ( 2006b): Conversion of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease predicted by hippocampal atrophy maps. Arch Neurol 63: 693–699. - PubMed
-
- Apostolova LG, Mosconi L, Thompson PM, Green AE, Hwang KS, Ramirez A, Mistur R, Tsui WH, de Leon MJ ( 2008): Subregional hippocampal atrophy predicts future decline to Alzheimer's dementia in cognitively normal subjects. Neurobiol Aging (epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging. 2008.08.008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bobinski M, Wegiel J, Wisniewski HM, Tarnawski M, Reisberg B, Mlodzik B, de Leon MJ, Miller DC ( 1995): Atrophy of hippocampal formation subdivisions correlates with stage and duration of Alzheimer disease. Dementia 6: 205–210. - PubMed
-
- Bobinski M, Wegiel J, Tarnawski M, Bobinski M, Reisberg B, de Leon MJ, Miller DC, Wisniewski HM ( 1997): Relationships between regional neuronal loss and neurofibrillary changes in the hippocampal formation and duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56: 414–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG0210028/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG10483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 RR019771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EB01651/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- AG16570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR019771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG026803/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR021813/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021028/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- LM05639/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071940/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG10129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013642/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

