Surgical outcome after docetaxel-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally-advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 20143466
- PMCID: PMC2825334
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.868
Surgical outcome after docetaxel-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally-advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
Aim: To investigate feasibility, morbidity and surgical mortality of a docetaxel-based chemotherapy regimen randomly administered before or after gastrectomy in patients suffering from locally-advanced resectable gastric cancer.
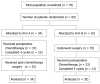
Methods: Patients suffering from locally-advanced (T3-4 any N M0 or any T N1-3 M0) gastric carcinoma, staged with endoscopic ultrasound, bone scan, computed tomography, and laparoscopy, were assigned to receive four 21 d/cycles of TCF (docetaxel 75 mg/m(2) day 1, cisplatin 75 mg/m(2) day 1, and fluorouracil 300 mg/m(2) per day for days 1-14), either before (Arm A) or after (Arm B) gastrectomy. Operative morbidity, overall mortality, and severe adverse events were compared by intention-to-treat analysis.
Results: From November 1999 to November 2005, 70 patients were treated. After preoperative TCF (Arm A), thirty-two (94%) resections were performed, 85% of which were R0. Pathological response was complete in 4 patients (11.7%), and partial in 18 (55%). No surgical mortality and 28.5% morbidity rate were observed, similar to those of immediate surgery arm (P = 0.86). Serious chemotherapy adverse events tended to be more frequent in arm B (23% vs 11%, P = 0.07), with a single death per arm.
Conclusion: Surgery following docetaxel-based chemotherapy was safe and with similar morbidity to immediate surgery in patients with locally-advanced resectable gastric carcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Forman D, Burley VJ. Gastric cancer: global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk factors. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;20:633–649. - PubMed
-
- Briasoulis E, Liakakos T, Dova L, Fatouros M, Tsekeris P, Roukos DH, Kappas AM. Selecting a specific pre- or postoperative adjuvant therapy for individual patients with operable gastric cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006;6:931–939. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi E, et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4991–4997. - PubMed
-
- Roth AD, Fazio N, Stupp R, Falk S, Bernhard J, Saletti P, Köberle D, Borner MM, Rufibach K, Maibach R, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil; docetaxel and cisplatin; and epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil as systemic treatment for advanced gastric carcinoma: a randomized phase II trial of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3217–3223. - PubMed