Betaine inhibits toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats with ethanol-induced liver injury
- PMID: 20143470
- PMCID: PMC2825338
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.897
Betaine inhibits toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats with ethanol-induced liver injury
Abstract
Aim: To test whether ethanol feeding could induce Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) responses, assess the hepatoprotective effect of betaine and its inhibitive effect on TLR4 in animal models of alcoholic liver injury.
Methods: Forty-eight female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups as control, model, low and high dose betaine groups. Except control group, all rats were fed with high fat-containing diet plus ethanol and fish oil gavages for 8 wk. Betaine was administered intragastrically after exposure of ethanol for 4 wk. The changes of liver histology were examined. The expression of TLR4 mRNA and protein was detected by RT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. The serum aminotransferase activity [alanine transarninase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST)], serum endotoxin, and liver inflammatory factors [tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), interleukin-18 (IL-18)] were also assayed.
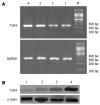
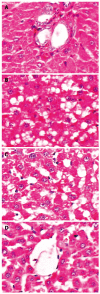
Results: Compared with control group, rats of model group developed marked liver injury, accompanied by an increase of ALT (159.41 +/- 7.74 U/L vs 59.47 +/- 2.34 U/L, P < 0.0001), AST (248.25 +/- 1.40 U/L vs 116.89 +/- 3.48 U/L, P < 0.0001), endotoxin (135.37 +/- 30.17 ng/L vs 44.15 +/- 7.54 ng/L, P < 0.0001), TNF-alpha (20.81 +/- 8.58 pg/mL vs 9.34 +/- 2.57 pg/mL, P = 0.0003), IFN-gamma (30.18 +/- 7.60 pg/mL vs 16.86 +/- 9.49 pg/mL, P = 0.0039) and IL-18 (40.99 +/- 8.25 pg/mL vs 19.73 +/- 9.31 pg/mL, P = 0.0001). At the same time, the expression of TLR4 mRNA and protein was markedly induced in the liver after chronic ethanol consumption (1.45 +/- 0.07 vs 0.44 +/- 0.04, P < 0.0001; 1.83 +/- 0.13 vs 0.56 +/- 0.08, P < 0.0001). Compared with model group, betaine feeding resulted in significant decreases of ALT (64.93 +/- 6.06 U/L vs 159.41 +/- 7.74 U/L, P < 0.0001), AST (188.73 +/- 1.11 U/L vs 248.25 +/- 1.40 U/L, P < 0.0001), endotoxin (61.80 +/- 12.56 ng/L vs 135.37 +/- 30.17 ng/L, P < 0.0001), TNF-alpha (9.79 +/- 1.32 pg/mL vs 20.81 +/- 8.58 pg/mL, P = 0.0003), IFN-gamma (18.02 +/- 5.96 pg/mL vs 30.18 +/- 7.60 pg/mL, P = 0.0008) and IL-18 (18.23 +/- 7.01 pg/mL vs 40.99 +/- 8.25 pg/mL, P < 0.0001). Betaine also improved liver steatosis. The expression levels of TLR4 mRNA or protein in liver tissues were significantly lowered (0.62 +/- 0.04 vs 1.45 +/- 0.07, P < 0.0001; and 0.65 +/- 0.06 vs 1.83 +/- 0.13, P < 0.0001). There was a statistical difference of TLR4 mRNA and protein expression between high- and low-dose betaine groups (0.62 +/- 0.04 vs 0.73 +/- 0.05, P < 0.0001, and 0.65 +/- 0.06 vs 0.81 +/- 0.09, P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Betaine can prevent the alcohol-induced liver injury effectively and improve the liver function. The expression of TLR4 increases significantly in ethanol-fed rats and betaine administration can inhibit TLR4 expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in the mechanism of early alcohol-induced liver injury in mice.Hepatology. 2001 Jul;34(1):101-8. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.25350. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11431739
-
Effects of traditional chinese medicine on endotoxin and its receptors in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Inflammation. 2008 Apr;31(2):121-32. doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9057-3. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Inflammation. 2008. PMID: 18302012
-
Betaine protects against high-fat-diet-induced liver injury by inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 and Toll-like receptor 4 expression in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Nov;58(11):3198-206. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2775-x. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23861108
-
Preventive and therapeutic role of betaine in liver disease: A review on molecular mechanisms.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;912:174604. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174604. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34743980 Review.
-
Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Mar;27 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):89-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07003.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22320924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of plasma functionalized polypropylene wound dressing for betaine hydrochloride controlled drug delivery on diabetic wounds.Sci Rep. 2021 May 5;11(1):9641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89105-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33953292 Free PMC article.
-
Uncarboxylated osteocalcin ameliorates hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in KKAy mice via activating insulin signaling pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Mar;41(3):383-393. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0311-z. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 31659239 Free PMC article.
-
Betaine inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 responses and restores intestinal microbiota in acute liver failure mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 14;10(1):21850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78935-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33318565 Free PMC article.
-
Silymarin's Protective Effects and Possible Mechanisms on Alcoholic Fatty Liver for Rats.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013 Jul 30;21(4):264-9. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2013.020. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013. PMID: 24244810 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress in chronic liver diseases and its mitigation by medicinal plants.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6321-6341. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fukui H. Relation of endotoxin, endotoxin binding proteins and macrophages to severe alcoholic liver injury and multiple organ failure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:172S–179S. - PubMed
-
- Fang ZH, Cui JW, Hu YY. [Endotoxin injury in alcoholic liver disease] Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi. 2005;13:636–638. - PubMed
-
- Xu FL, You HB, Li XH, Chen XF, Liu ZJ, Gong JP. Glycine attenuates endotoxin-induced liver injury by downregulating TLR4 signaling in Kupffer cells. Am J Surg. 2008;196:139–148. - PubMed
-
- Enomoto N, Takei Y, Yamashima S, Ikejima K, Kitamura T, Sato N. Protective effect of pioglitazone against endotoxin-induced liver injury through prevention of Kupffer cell sensitization. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:216S–219S. - PubMed
-
- Dai Q, Pruett SB. Ethanol suppresses LPS-induced Toll-like receptor 4 clustering, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, and associated TNF-alpha production. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006;30:1436–1444. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

