Proton affinity of the oxyanion hole in the active site of ketosteroid isomerase
- PMID: 20143849
- PMCID: PMC2852583
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100074s
Proton affinity of the oxyanion hole in the active site of ketosteroid isomerase
Abstract
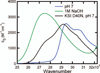
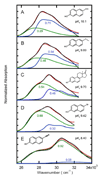
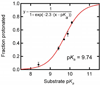
The absorption spectra of a series of inhibitors bound at the active site of Delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas putida were found to exhibit substantial variations in the contributions of the protonated and deprotonated forms. Systematic variation of the inhibitor solution pK(a) combined with a method of quantifying the contributions of each protonation state showed the oxyanion hole in the active site of wild-type Delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase to have a proton affinity equal to a solution pK(a) of 10.05 +/- 0.03, which is similar to the measured pK(a) (10.0) of the reaction intermediate. This observation supports the prediction of Cleland, Kreevoy, Frey, Gassman, and Gerlt that an enzyme utilizing a strong hydrogen bond for catalysis matches the proton affinity of the protein to the intermediate [Cleland, W. W., and Kreevoy, M. M. (1994) Science 264, 1887-1890; Frey, P. A., Whitt, S., and Tobin, J. (1994) Science 264, 1927-1930; Gerlt, J. A., and Gassman, P. G. (1993) Biochemistry 32, 11934-11952]. As the difference in proton affinity decreases, the strength of the hydrogen bond increases, and the closely matched proton affinity between the active site and the reaction intermediate supports the possibility that a short, strong hydrogen bond is catalytically relevant in Delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase.
Figures
References
-
- Gerlt JA, Gassman PG. Understanding the rates of certain enzyme-catalyzed reactions: Proton abstraction from carbon acids, acyl transfer reactions, and displacement reactions of phosphodiesters. Biochemistry. 1993;32:11934–11952. - PubMed
-
- Gerlt JA, Gassman PG. An explanation for rapid enzyme-catalyzed proton abstraction from carbon acids: importance of late transition states in concerted mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993;115:11552–11568.
-
- Cleland WW, Kreevoy MM. Low-barrier hydrogen bonds and enzymic catalysis. Science. 1994;264:1887–1890. - PubMed
-
- Frey PA, Whitt S, Tobin J. A low-barrier hydrogen bond in the catalytic triad of serine proteases. Science. 1994;264:1927–1930. - PubMed
-
- Pollack RM. Enymatic mechanisms for catalysis of enolization: ketosteroid isomerase. Bioorg. Chem. 2004;32:341–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

