A conserved mode of protein recognition and binding in a ParD-ParE toxin-antitoxin complex
- PMID: 20143871
- PMCID: PMC2846751
- DOI: 10.1021/bi902133s
A conserved mode of protein recognition and binding in a ParD-ParE toxin-antitoxin complex
Abstract
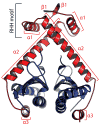
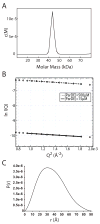
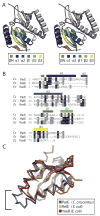
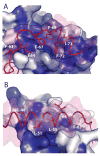
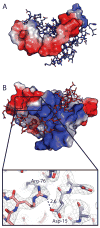
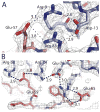
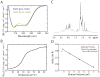
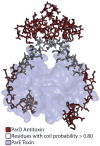
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems form a ubiquitous class of prokaryotic proteins with functional roles in plasmid inheritance, environmental stress response, and cell development. ParDE family TA systems are broadly conserved on plasmids and bacterial chromosomes and have been well characterized as genetic elements that promote stable plasmid inheritance. We present a crystal structure of a chromosomally encoded ParD-ParE complex from Caulobacter crescentus at 2.6 A resolution. This TA system forms an alpha(2)beta(2) heterotetramer in the crystal and in solution. The toxin-antitoxin binding interface reveals extensive polar and hydrophobic contacts of ParD antitoxin helices with a conserved recognition and binding groove on the ParE toxin. A cross-species comparison of this complex structure with related toxin structures identified an antitoxin recognition and binding subdomain that is conserved between distantly related members of the RelE/ParE toxin superfamily despite a low level of overall primary sequence identity. We further demonstrate that ParD antitoxin is dimeric, stably folded, and largely helical when not bound to ParE toxin. Thus, the paradigmatic model in which antitoxin undergoes a disorder-to-order transition upon toxin binding does not apply to this chromosomal ParD-ParE TA system.
Figures

References
-
- Gronlund H, Gerdes K. Toxin-antitoxin systems homologous with relBE of Escherichia coli plasmid P307 are ubiquitous in prokaryotes. J Mol Biol. 1999;285:1401–1415. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Lobner-Olesen A. Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:371–382. - PubMed
-
- Buts L, Lah J, Dao-Thi MH, Wyns L, Loris R. Toxin-antitoxin modules as bacterial metabolic stress managers. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:672–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

