Vimentin is a functional partner of hormone sensitive lipase and facilitates lipolysis
- PMID: 20143880
- PMCID: PMC2849902
- DOI: 10.1021/pr900909t
Vimentin is a functional partner of hormone sensitive lipase and facilitates lipolysis
Abstract
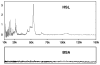
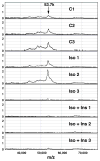
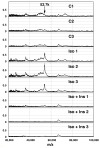
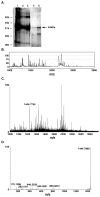
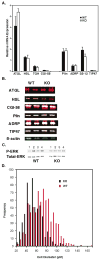
Lipolysis involves a number of components including signaling pathways, droplet-associated proteins, and lipases such as hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL). We used surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectroscopy to identify cellular proteins that might interact with HSL and potentially influence lipolysis. Using recombinant HSL as bait on protein chips, clusters of proteins of 14.7-18.9, 25.8-26.8, 36.1, 44.3-49.1, and 53.7 kDa were identified that interact with HSL, particularly when lysates were examined from beta-agonist treated mouse adipocytes. The ability to detect these interacting proteins was markedly diminished when the adipocytes were treated with insulin. A very similar pattern of proteins was identified when anti-HSL IgG was used as the bait. Following immunocapture, the identification of the prominent 53.7 kDa protein was carried out by tryptic digestion and MS analysis and determined to be vimentin. The interaction of HSL with vimentin, and its hormonal dependence, was confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation. beta-Agonist stimulated lipolysis and the rate of HSL translocation were impaired in vimentin null adipocytes, even though normal amounts of lipases and droplet-associated proteins are expressed. The current studies provide evidence that vimentin participates in lipolysis through direct, hormonally regulated interactions with HSL.
Figures
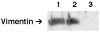

References
-
- Greenberg AS, Shen W-J, Muliro K, Patel S, Souza SC, Roth RA, Kraemer FB. Stimulation of lipolysis and hormone-sensitive lipase via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(48):45456–45461. - PubMed
-
- Robidoux J, Kumar N, Daniel KW, Moukdar F, Cyr M, Medvedev AV, Collins S. Maximal beta3-adrenergic regulation of lipolysis involves Src and epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(49):37794–802. - PubMed
-
- Kraemer FB, Shen W-J. Hormone-sensitive lipase: control of intracellular tri-(di-) acylglycerol and cholesteryl ester hydrolysis. J Lipid Res. 2002;43(10):1585–1594. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg AS, Egan JJ, Wek SA, Garty NB, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Londos C. Perilipin, a major hormonally regulated adipocyte-specific phosphoprotein associated with the periphery of lipid storage droplets. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(17):11341–11346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

