Effects of hyperinsulinemia on lipolytic function of three-dimensional adipocyte/endothelial co-cultures
- PMID: 20144013
- PMCID: PMC2943403
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2009.0760
Effects of hyperinsulinemia on lipolytic function of three-dimensional adipocyte/endothelial co-cultures
Abstract
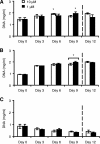
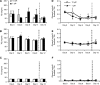
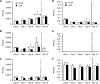
The increased incidence of both type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity has prompted the need to develop physiologically relevant adipose tissue models for controlled study of both normal and diseased adipose functions. Insulin resistance, characteristic of both type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, is often preceded by hyperinsulinemia. We propose here a three-dimensional (3D) co-culture adipose tissue model to study the effects of high insulin exposure, which enabled the study of physiological cell responses to hyperinsulinemic conditions. Two-dimensional adipocyte studies were initially conducted to establish a baseline control in which insulin levels were established. Adipocytes and endothelial cells were subsequently co-cultured on 3D porous silk fibroin scaffolds in normal or high insulin concentrations, and their physiological responses were assessed with respect to lipogenesis and lipolysis. High insulin levels stimulated both an increase in triglyceride accumulation and a decrease in lipolysis levels compared to that of normal insulin conditions. In contrast, adipocyte monocultures did not exhibit any differences between insulin levels. The ability of this 3D system to elicit physiological responses to hyperinsulinemia in co-culture serves as a significant step forward in adipose tissue engineering. The development of physiologically relevant 3D in vitro adipose tissue models presents promise for the study of disease mechanisms as well as in assessing therapeutic treatments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipolytic function of adipocyte/endothelial cocultures.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011 May;17(9-10):1437-44. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2010.0527. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011. PMID: 21247356 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of adipocyte size and adipose depot on the in vitro lipolytic activity and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue in dairy cows at the end of the dry period.J Dairy Sci. 2016 Mar;99(3):2319-2328. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10440. Epub 2015 Dec 24. J Dairy Sci. 2016. PMID: 26723122
-
Recombinant human FIZZ3/resistin stimulates lipolysis in cultured human adipocytes, mouse adipose explants, and normal mice.Endocrinology. 2005 May;146(5):2200-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1421. Epub 2005 Feb 10. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15705777
-
Adipose tissue lipolysis as a metabolic pathway to define pharmacological strategies against obesity and the metabolic syndrome.Pharmacol Res. 2006 Jun;53(6):482-91. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2006.03.009. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Pharmacol Res. 2006. PMID: 16644234 Review.
-
Adipocyte lipolysis and insulin resistance.Biochimie. 2016 Jun;125:259-66. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.10.024. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26542285 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the role of plexin D1 in body fat distribution and susceptibility to metabolic disease using a zebrafish model system.Adipocyte. 2017 Oct 2;6(4):277-283. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2017.1356504. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Adipocyte. 2017. PMID: 28792859 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Silk as a Scaffold for Mature, Sustainable Unilocular Adipose 3D Tissue Engineered Systems.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016 Jul;5(13):1667-77. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600211. Epub 2016 May 19. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016. PMID: 27197588 Free PMC article.
-
3D bioprinted white adipose model forin vitrostudy of cancer-associated cachexia induced adipose tissue remodeling.Biofabrication. 2022 May 26;14(3):10.1088/1758-5090/ac6c4b. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac6c4b. Biofabrication. 2022. PMID: 35504266 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Three-Dimensional Adipose Tissue Model for Studying Embryonic Exposures to Obesogenic Chemicals.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Jul;45(7):1807-1818. doi: 10.1007/s10439-016-1752-x. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27815650 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Determines Lipotoxicity and Triggers the Metabolic Syndrome: Current Challenges and Clinical Perspectives.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:231-272. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287854 Review.
References
-
- Kahn S.E. Hull R.L. Utzschneider K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444:840. - PubMed
-
- Foster-Schubert K.E. Cummings D.E. Emerging therapeutic strategies for obesity. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:779. - PubMed
-
- Cohen A. Horton E.S. Progress in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: new pharmacologic approaches to improve glycemic control. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23:905. - PubMed
-
- Levetan C. Oral antidiabetic agents in type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23:945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

