Parameters for accurate genome alignment
- PMID: 20144198
- PMCID: PMC2829014
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-80
Parameters for accurate genome alignment
Abstract
Background: Genome sequence alignments form the basis of much research. Genome alignment depends on various mundane but critical choices, such as how to mask repeats and which score parameters to use. Surprisingly, there has been no large-scale assessment of these choices using real genomic data. Moreover, rigorous procedures to control the rate of spurious alignment have not been employed.
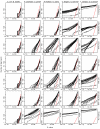
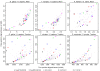
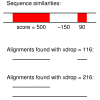
Results: We have assessed 495 combinations of score parameters for alignment of animal, plant, and fungal genomes. As our gold-standard of accuracy, we used genome alignments implied by multiple alignments of proteins and of structural RNAs. We found the HOXD scoring schemes underlying alignments in the UCSC genome database to be far from optimal, and suggest better parameters. Higher values of the X-drop parameter are not always better. E-values accurately indicate the rate of spurious alignment, but only if tandem repeats are masked in a non-standard way. Finally, we show that gamma-centroid (probabilistic) alignment can find highly reliable subsets of aligned bases.
Conclusions: These results enable more accurate genome alignment, with reliability measures for local alignments and for individual aligned bases. This study was made possible by our new software, LAST, which can align vertebrate genomes in a few hours http://last.cbrc.jp/.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

