Computational prediction and experimental validation of evolutionarily conserved microRNA target genes in bilaterian animals
- PMID: 20144220
- PMCID: PMC2833159
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-101
Computational prediction and experimental validation of evolutionarily conserved microRNA target genes in bilaterian animals
Abstract
Background: In many eukaryotes, microRNAs (miRNAs) bind to complementary sites in the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and regulate their expression at the stage of translation. Recent studies have revealed that many miRNAs are evolutionarily conserved; however, the evolution of their target genes has yet to be systematically characterized. We sought to elucidate a set of conserved miRNA/target-gene pairs and to analyse the mechanism underlying miRNA-mediated gene regulation in the early stage of bilaterian evolution.
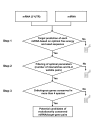
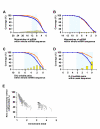
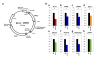
Results: Initially, we extracted five evolutionarily conserved miRNAs (let-7, miR-1, miR-124, miR-125/lin-4, and miR-34) among five diverse bilaterian animals. Subsequently, we designed a procedure to predict evolutionarily conserved miRNA/target-gene pairs by introducing orthologous gene information. As a result, we extracted 31 orthologous miRNA/target-gene pairs that were conserved among at least four diverse bilaterian animals; the prediction set showed prominent enrichment of orthologous miRNA/target-gene pairs that were verified experimentally. Approximately 84% of the target genes were regulated by three miRNAs (let-7, miR-1, and miR-124) and their function was classified mainly into the following categories: development, muscle formation, cell adhesion, and gene regulation. We used a reporter gene assay to experimentally verify the downregulation of six candidate pairs (out of six tested pairs) in HeLa cells.
Conclusions: The application of our new method enables the identification of 31 miRNA/target-gene pairs that were expected to have been regulated from the era of the common bilaterian ancestor. The downregulation of all six candidate pairs suggests that orthologous information contributed to the elucidation of the primordial set of genes that has been regulated by miRNAs; it was also an efficient tool for the elimination of false positives from the predicted candidates. In conclusion, our study identified potentially important miRNA-target pairs that were evolutionarily conserved throughout diverse bilaterian animals and that may provide new insights into early-stage miRNA functions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifications of conserved 7-mers in 3'-UTRs and microRNAs in Drosophila.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Nov 8;8:432. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-432. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17996040 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification and experimental validation of microRNAs binding to the Alzheimer-related gene ADAM10.BMC Med Genet. 2012 May 17;13:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-13-35. BMC Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22594617 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Drosophila MicroRNA targets.PLoS Biol. 2003 Dec;1(3):E60. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0000060. Epub 2003 Oct 13. PLoS Biol. 2003. PMID: 14691535 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
Genomic organization of microRNAs.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;222(3):540-5. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21993. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20020507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Amblyomma americanum microRNAs in response to Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection and their potential role in vectorial capacity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 17;14:1427562. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1427562. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39086604 Free PMC article.
-
Germline stem cell integrity and quiescence are controlled by an AMPK-dependent neuronal trafficking pathway.PLoS Genet. 2023 Apr 14;19(4):e1010716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010716. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37058536 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, expression, and molecular evolution of microRNAs in the "living fossil" Triops cancriformis (tadpole shrimp).RNA. 2015 Feb;21(2):230-42. doi: 10.1261/rna.045799.114. Epub 2014 Dec 18. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25525151 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Biology Reveals MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Regulation.Front Genet. 2011 Jun 23;2:29. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2011.00029. eCollection 2011. Front Genet. 2011. PMID: 22303325 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and characterization of microRNAs from eleven fish species by computational methods.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2015 Jul;22(4):374-81. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26150741 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

