Oral insulin: the rationale for this approach and current developments
- PMID: 20144296
- PMCID: PMC2769870
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300322
Oral insulin: the rationale for this approach and current developments
Abstract
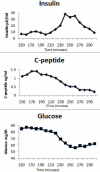
Insulin remains the most effective and durable hypoglycemic agent for the treatment of diabetes. The addition of an effective oral insulin dosage form to the antidiabetes armamentarium may have significant benefits in terms of fostering compliance and adherence among patients, as well as physiologic advantages due to the fact that such a dosage form replicates the natural route of insulin secretion and absorption through the portal vein and targets the liver directly. Several companies have developed technological platforms that protect polypeptides and proteins from enzymatic hydrolysis, enable their transport across the epithelial lining, and promote their absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. A review of the potential physiological rationale and advantages, as well as of current pertinent technologies used specifically with insulin, is herewith provided.
2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures

References
-
- Meier JJ, Holst JJ, Schmidt WE, Nauck MA. Reduction of hepatic insulin clearance after oral glucose ingestion is not mediated by glucagon-like peptide 1 or gastric inhibitory polypeptide in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293(3):E849–E856. - PubMed
-
- Eaton RP, Allen RC, Schade DS. Hepatic removal of insulin in normal man: dose response to endogenous insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983;56(6):1294–1300. - PubMed
-
- Meistas MT, Rendell M, Margolis S, Kowarski AA. Estimation of the secretion rate of insulin from the urinary excretion rate of C-peptide. Study in obese and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1982;31(5 Pt 1):449–453. - PubMed
-
- Satake S, Moore MC, Igawa K, Converse M, Farmer B, Neal DW, Cherrington AD. Direct and indirect effects of insulin on glucose uptake and storage by the liver. Diabetes. 2002;51(6):1663–1671. - PubMed
-
- Camacho RC, Pencek RR, Lacy DB, James FD, Wasserman DH. Suppression of endogenous glucose production by mild hyperinsulinemia during exercise is determined predominantly by portal venous insulin. Diabetes. 2004;53(2):285–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

