The prevention of type 2 diabetes: an overview
- PMID: 20144325
- PMCID: PMC2769939
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300423
The prevention of type 2 diabetes: an overview
Abstract
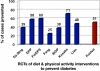
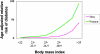
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is one of the major public health threats in the United States today, reaching epidemic rates. Epidemiological evidence suggests a strong link between obesity and the risk of developing diabetes. Increasing evidence demonstrates that lifestyle interventions can significantly delay or possibly prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes in persons with increased risk. Despite these findings, there remain important barriers to the translation of this research to the public health. These include identifying persons with an increased risk for developing the disease and the lack of easily accessible, cost-effective intervention programs. At least one study, however, has effectively implemented an evidenced-based intervention in community settings, suggesting that it may be possible to develop a model for the national scalability of primary prevention in the United States.
Copyright 2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
References
-
- National Diabetes Fact Sheet: general information and national estimates on diabetes in the United States, 2003. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [cited 2004 May 5] Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2003.pdf.
-
- Diabetes: disabling, deadly, and on the rise. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Health and Human Services [cited 2004 Apr 15] Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/aag/pdf/aag_ddt2004.pdf.
-
- Harris MI, Flegal KM, Cowie CC, Eberhardt MS, Goldstein DE, Little RR, Wiedmeyer HM, Byrd-Holt DD. Prevalence of diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance in U.S. adults. The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(4):518–524. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Bowman BA, Ford ES, Vinicor F, Marks JS, Koplan JP. The continuing epidemics of obesity and diabetes in the United States. JAMA. 2001;286(10):1195–1200. - PubMed
-
- National Diabetes Fact Sheet. American Diabetes Association [cited 2004 May 2] Available from: http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-statistics/national-diabetes-fact-sheet....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical