Factors affecting blood glucose monitoring: sources of errors in measurement
- PMID: 20144340
- PMCID: PMC2769960
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300438
Factors affecting blood glucose monitoring: sources of errors in measurement
Abstract
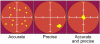
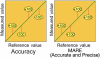
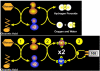
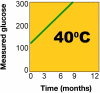
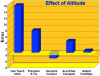
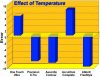
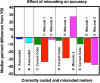
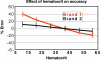
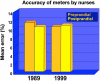
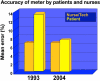
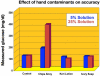
Glucose monitoring has become an integral part of diabetes care but has some limitations in accuracy. Accuracy may be limited due to strip manufacturing variances, strip storage, and aging. They may also be due to limitations on the environment such as temperature or altitude or to patient factors such as improper coding, incorrect hand washing, altered hematocrit, or naturally occurring interfering substances. Finally, exogenous interfering substances may contribute errors to the system evaluation of blood glucose. In this review, I discuss the measurement of error in blood glucose, the sources of error, and their mechanism and potential solutions to improve accuracy in the hands of the patient. I also discuss the clinical measurement of system accuracy and methods of judging the suitability of clinical trials and finally some methods of overcoming the inaccuracies. I have included comments about additional information or education that could be done today by manufacturers in the appropriate sections. Areas that require additional work are discussed in the final section.
Copyright 2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures


References
-
- Bergenstal RM, Gavin JR., III Global Consensus Conference on Glucose Monitoring Panel. The role of self-monitoring of blood glucose in the care of people with diabetes: report of a global consensus conference; Am J Med; 2005. pp. 1S–6S. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch IB, Bode BW, Childs BP, Close KL, Fisher WA, Gavin JR, Ginsberg BH, Raine CH, Verderese CA. Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in insulin- and non-insulin-using adults with diabetes: consensus recommendations for improving SMBG accuracy, utilization, and research. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008;10(6):419–439. - PubMed
-
- International Organization for Standardization. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization; 2003. In vitro diagnostic test systems. Requirements for blood-glucose monitoring system for self-testing in managing diabetes mellitus. Reference number ISO 15197:2003 (E)
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 1):S12–S54. - PubMed
-
- Boyd JC, Bruns DE. Quality specifications for glucose meters: assessment by simulation modeling of errors in insulin dose. Clin Chem. 2001;47(2):209–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

