Glycemic control in the burn intensive care unit: focus on the role of anemia in glucose measurement
- PMID: 20144386
- PMCID: PMC2787032
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300612
Glycemic control in the burn intensive care unit: focus on the role of anemia in glucose measurement
Abstract
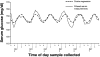
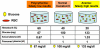
Glycemic control with intensive insulin therapy (IIT) has received widespread adoption secondary to findings of improved clinical outcomes and survival in the burn population. Severe burn as a model for trauma is characterized by a hypermetabolic state, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance. In this article, we review the findings of a burn center research facility in terms of understanding glucose management. The conferred benefits from IIT, our findings of poor outcomes associated with glycemic variability, advantages from preserved diurnal variation of glucose and insulin, and impacts of glucometer error and hematocrit correction factor are discussed. We conclude with direction for further study and the need for a reliable continuous glucose monitoring system. Such efforts will further the endeavor for achieving adequate glycemic control in order to assess the efficacy of target ranges and use of IIT.
Figures

References
-
- Gale SC, Sicoutris C, Reilly PM, Schwab CW, Gracias VH. Poor glycemic control is associated with increased mortality in critically ill trauma patients. Am Surg. 2007;73(5):454–460. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi GY, Murad MH, Flynn DN, Erwin PJ, Cavalcante AB, Bay Nielsen H, Capes SE, Thorlund K, Montori VM, Devereaux PJ. Effect of perioperative insulin infusion on surgical morbidity and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(4):418–430. - PubMed
-
- Krinsley JS. Effect of an intensive glucose management protocol on the mortality of critically ill adult patients. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004;79(8):992–1000. - PubMed
-
- Pittas AG, Siegel RD, Lau J. Insulin therapy for critically ill hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(19):2005–2011. - PubMed
-
- Reed CC, Stewart RM, Sherman M, Myers JG, Corneille MG, Larson N, Gerhardt S, Beadle R, Gamboa C, Dent D, Cohn SM, Pruitt BA., Jr. Intensive insulin protocol improves glucose control and is associated with a reduction in intensive care unit mortality. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204(5):1048–1055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

