Glucose clamp algorithms and insulin time-action profiles
- PMID: 20144413
- PMCID: PMC2769898
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300503
Glucose clamp algorithms and insulin time-action profiles
Abstract
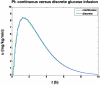
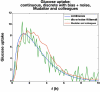
Motivation: Most current insulin pumps include an insulin-on-board (IOB) feature to help subjects avoid problems associated with "insulin stacking." In addition, many control algorithms proposed for a closed-loop artificial pancreas make use of IOB to reduce the probability of hypoglycemic events that often occur due to the integral action of the controller. The IOB curves are generated from the pharmacodynamic (time-activity profiles) actions of subcutaneous insulin, which are obtained from glycemic clamp studies.
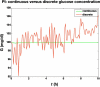
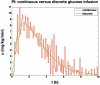
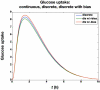
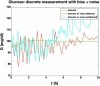
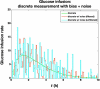
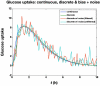
Methods: Glycemic clamp algorithms are reviewed and in silico studies are performed to analyze the effect of glucose meter bias and noise on glycemic control and the manipulated glucose infusion rates. The glucose infusion rates are used to obtain insulin time-activity profiles, which are then used to generate IOB curves.
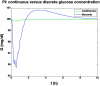
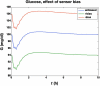
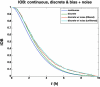
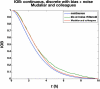
Results: A model-based, three-step-ahead controller is shown to be equivalent to a proportional-integral control algorithm with time-delay compensation. A systematic glucose meter bias of +6 mg/dl results in a decrease in the glucose area under the curve of 3% but no change in the IOB profiles.
Conclusions: Based on these preliminary simulation studies, a substantial amount of glucose meter bias and noise during a glycemic clamp can be tolerated with little net effect on the IOB curves. It is suggested that handheld glucose meters can therefore be used in clamp studies if the measurements are filtered (averaged) before processing by the control algorithm. Clinical studies are needed to confirm these preliminary results.
2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
References
-
- Lee H, Buckingham BA, Bequette BW. An insulin-on-board formulation of a proportional-integral-derivative controller for a closed-loop artificial pancreas. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009;3(2):A101.
-
- Walsh J, Roberts R. 4th ed. San Diego: Torrey Pines Press; 2006. Pumping insulin.
-
- Zisser H, Robinson L, Bevier W, Dassau E, Ellingsen C, Doyle FJ, Jovanovic L. Bolus calculator: a review of four “smart” insulin pumps. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008;10(6):441–444. - PubMed
-
- Heinemann L. Mainz: Verlag Kirchheim; 2004. Time-action profiles of insulin preparations. http://www.profil-research.de/downloads/publikationen/buch.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

