A novel adaptive basal therapy based on the value and rate of change of blood glucose
- PMID: 20144423
- PMCID: PMC2769919
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300513
A novel adaptive basal therapy based on the value and rate of change of blood glucose
Abstract
Background: Modern insulin pump therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus offers the freedom to program several basal profiles that may accommodate diurnal ariability in insulin sensitivity and activity level. However, these basal profiles do not change even if a pending hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic event is foreseen. New insulin pumps could receive a direct feed of glucose values from a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system and could enable dynamic basal adaptation to improve glycemic control.
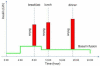
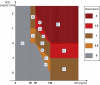
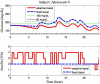
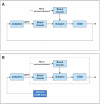
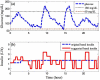
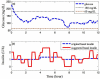
Method: The proposed method is a two-step procedure. After the design of an initial basal profile, an adaptation of the basal rate is suggested as a gain multiplier based on the current CGM glucose value and its rate of change (ROC). Taking the glucose value and its ROC as axes, a two-dimensional plane is divided into a nine-zone mosaic, where each zone is given a predefined basal multiplier; for example, a basal multiplier of zero indicates a recommendation to shut off the pump.
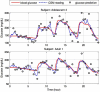
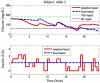
Results: The proposed therapy was evaluated on 20 in silico subjects (ten adults and ten adolescents) in the Food and Drug Administration-approved UVa/Padova simulator. Compared with conventional basal therapy, the proposed basal adjustment improved the percentage of glucose levels that stayed in the range of 60-180 mg/dl for all 20 subjects. In addition, the adaptive basal therapy reduced the average blood glucose index values.
Conclusions: The proposed therapy provides the flexibility to account for insulin sensitivity variations that may result from stress and/or physical activities. Because of its simplicity, the proposed method could be embedded in a chip in a future artificial pancreatic beta cell or used in a "smart" insulin pump.
2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures

References
-
- Zisser H, Robinson L, Bevier W, Dassau E, Ellingsen C, Doyle FJ, Jovanovic L. Bolus calculator: a review of four “smart” insulin pumps. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2008;10(6):441–444. - PubMed
-
- Jovanovič L. Insulin therapy and algorithms for treating type 1 diabetes mellitus. In: Optimizing insulin therapy in patients with diabetes. CME Activity jointly sponsored by Washington Hospital Center and MedStar Research Institute. 2002:13–19.
-
- Chia CW, Saudek CD. Glucose sensors: toward closed loop insulin delivery. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004;33(1):175–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

