Delays in minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring devices: a review of current technology
- PMID: 20144438
- PMCID: PMC2769894
- DOI: 10.1177/193229680900300528
Delays in minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring devices: a review of current technology
Abstract
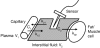
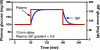
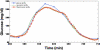
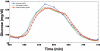
Through the use of enzymatic sensors-inserted subcutaneously in the abdomen or ex vivo by means of microdialysis fluid extraction-real-time minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices estimate blood glucose by measuring a patient's interstitial fluid (ISF) glucose concentration. Signals acquired from the interstitial space are subsequently calibrated with capillary blood glucose samples, a method that has raised certain questions regarding the effects of physiological time lags and of the duration of processing delays built into these devices. The time delay between a blood glucose reading and the value displayed by a continuous glucose monitor consists of the sum of the time lag between ISF and plasma glucose, in addition to the inherent electrochemical sensor delay due to the reaction process and any front-end signal processing delays required to produce smooth traces. Presented is a review of commercially available, minimally invasive continuous glucose monitors with manufacturer reported device delays. The data acquisition process for the Medtronic MiniMed (Northridge, CA) continuous glucose monitoring system-CGMS Gold-and the Guardian RT monitor is described with associated delays incurred for each processing step. Filter responses for each algorithm are examined using in vitro hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic clamps, as well as with an analysis of fast glucose excursions from a typical meal response. Results demonstrate that the digital filters used by each algorithm do not cause adverse effects to fast physiologic glucose excursions, although nonphysiologic signal characteristics can produce greater delays.
2009 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures


References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trials Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–986. - PubMed
-
- Mastrototaro JJ. The MiniMed continuous glucose monitoring system. J Pediatr Endoncrinol Metab. 1999;12:751–758. - PubMed
-
- Bode BW, Gross TM, Thornton KR, Mastrototaro JJ. Continuous glucose monitoring used to adjust diabetes therapy improves glycosylated hemoglobin: a pilot study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1999;46(3):183–189. - PubMed
-
- Gross TM, Bode BW, Einhorn D, Kayne DM, Reed JH, White NH, Mastrototaro JJ. Performance evaluation of the MiniMed continuous glucose monitoring system dur-ing patient home use. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2000;2(1):49–56. - PubMed
-
- Bode B, Gross K, Rikalo N, Schwartz S, Wahl T, Page C, Gross T, Mastrototaro J. Alarms based on real-time sensor glucose values alert patients to hypo- and hypergly-cemia: the guardian continuous monitoring system. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2004;6(2):105–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

