RTN/Nogo in forming Alzheimer's neuritic plaques
- PMID: 20144652
- PMCID: PMC2888855
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.01.017
RTN/Nogo in forming Alzheimer's neuritic plaques
Abstract
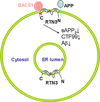
One of the pathological hallmarks in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the presence of neuritic plaques, in which amyloid deposits are surrounded by reactive gliosis and dystrophic neurites. Within neuritic plaques, reticulon 3 (RTN3), a homolog of Nogo protein, appears to regulate the formation of both amyloid deposition via negative modulation of BACE1 activity and dystrophic neurites via the formation of RTN3 aggregates. Transgenic mice over-expressing RTN3, but not the other known markers of dystrophic neurites in AD brain, spontaneously develop RTN3-immunoreactive dystrophic neurites. The presence of dystrophic neurites impairs cognition. Blocking abnormal RTN3 aggregation will increase the available RTN3 monomer and is therefore a promising therapeutic strategy for enhancing cognitive function in AD patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transgenic mice overexpressing reticulon 3 develop neuritic abnormalities.EMBO J. 2007 Jun 6;26(11):2755-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601707. Epub 2007 May 3. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17476306 Free PMC article.
-
BAP31 deficiency contributes to the formation of amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer's disease by reducing the stability of RTN3.FASEB J. 2019 Apr;33(4):4936-4946. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801702R. Epub 2018 Dec 31. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30596517
-
Accumulation of neutral lipids in dystrophic neurites surrounding amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Apr;1870(4):167086. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167086. Epub 2024 Feb 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 38378084 Free PMC article.
-
Neuritic Plaques - Gateways to Understanding Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May;61(5):2808-2821. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03736-7. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37940777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of altered RTN3 expression on BACE1 activity and Alzheimer's neuritic plaques.Rev Neurosci. 2017 Feb 1;28(2):145-154. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2016-0054. Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27883331 Review.
Cited by
-
The Alzheimer's β-secretase BACE1 localizes to normal presynaptic terminals and to dystrophic presynaptic terminals surrounding amyloid plaques.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Sep;126(3):329-52. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1152-3. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 23820808 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming translational barriers impeding development of Alzheimer's disease modifying therapies.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):224-236. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13583. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27145445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_0043947 contributes to interleukin 1β-induced injury in chondrocytes by sponging miR-671-5p to up-regulate RTN3 expression in osteoarthritis pathology.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Mar 24;17(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02970-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35331286 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Nogo-A/Nogo-A receptor in Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Jun;21(6):479-85. doi: 10.1111/cns.12387. Epub 2015 Mar 2. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 25732725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the earliest pathological changes of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(3):281-7. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151218150322. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26679855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes CA, Markowska AL, Ingram DK, Kametani H, Spangler EL, Lemken VJ, Olton DS. Acetyl-1-carnitine. 2: Effects on learning and memory performance of aged rats in simple and complex mazes. Neurobiol. Aging. 1990;11:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
-
- Cai Y, Saiyin H, Lin Q, Zhang P, Tang L, Pan X, Yu L. Identification of a new RTN3 transcript, RTN3-A1, and its distribution in adult mouse brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005;138:236–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

