Blockade of tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling in tumor-associated macrophages as a radiosensitizing strategy
- PMID: 20145121
- PMCID: PMC8849568
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2995
Blockade of tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling in tumor-associated macrophages as a radiosensitizing strategy
Abstract
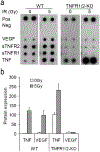
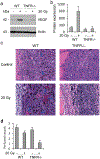
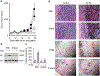
Most cancer patients receive radiotherapy during the course of their disease. Improvements in the therapeutic index have been based mainly on physical improvements in delivery, as radiosensitizer development to target tumor cells has yet to yield effective agents. Recent investigations have focused on the tumor stroma as a target for radiosensitization. Here, we report that depletion of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMvarphi) by systemic or local injection of the macrophage-depleting liposomal clodronate before radiotherapy can increase the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation (IR), either as a large single dose (20 Gy) or as a fractionated dose (2 Gy x 10). Coimplantation of tumor cells with bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMvarphi) increased tumor radioresistance. Studies using mice with germline deletions in tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 (TNFR1,2(-/-)) or TNFalpha (TNF(-/-)), or treatment of wild-type mice with a soluble TNF receptor fusion protein (Enbrel), revealed that radioresistance mediated by BMDMvarphi required intact TNFalpha signaling. Radiation exposure upregulated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in macrophages and VEGF-neutralizing antibodies enhanced the antitumor response to IR. Thus, the radioprotective effect of TNFalpha was mediated by TAM-produced VEGF. Our findings offer a mechanistic basis to target macrophage populations generally or TNFalpha-induced macrophage VEGF specifically as tractable strategies to improve the efficacy of radiotherapy.
Figures
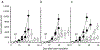
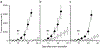
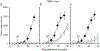
References
-
- Salama JK CS, Mehta N, Yenice KM, Stadler WM, Vokes EE, Haraf DJ, Hellman S, and Weichselbaum RR. An initial report of a radiation dose escalation trial in patients with one to five sites of metastatic disease. Clinical Cancer Research. 2008. - PubMed
-
- Vokes EE, Panje WR, Mick R, Kozloff MF, Moran WJ, Sutton HG, Goldman MD, Tybor AG, Weichselbaum RR. A randomized study comparing two regimens of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy in multimodal therapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. Cancer. 1990;66:206–13. - PubMed
-
- Masunaga S, Hirayama R, Uzawa A, Kashino G, Suzuki M, Kinashi Y, Liu Y, Koike S, Ando K, Ono K. The effect of post-irradiation tumor oxygenation status on recovery from radiation-induced damage in vivo: with reference to that in quiescent cell populations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:1109–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roses RE, Xu M, Koski GK, Czerniecki BJ. Radiation therapy and Toll-like receptor signaling: implications for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:200–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

