DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target
- PMID: 20145149
- PMCID: PMC3003295
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3263
DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target
Abstract
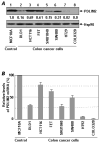
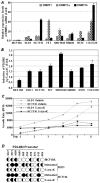
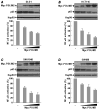
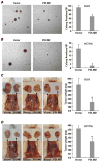
Constitutive activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) transcription factor plays a key role in chronic colonic inflammation and colon tumorigenesis. However, the mechanisms by which the tightly regulated NF-kappaB pathway becomes constitutively activated during colonic pathogenesis remain obscure. Here, we report that PDLIM2, an essential terminator of NF-kappaB activation, is repressed in various human colorectal cancer cell lines, suggesting one important mechanism for the constitutive activation of NF-kappaB. Indeed, expression of exogenous PDLIM2 inhibited constitutive NF-kappaB activation in these colorectal cancer cells. Importantly, the PDLIM2 expression was sufficient to suppress in vitro anchorage-independent growth and in vivo tumor formation of these malignant cells. We have further shown that the PDLIM2 repression involves promoter methylation. Accordingly, treatment of the colorectal tumor cell lines with the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine restored PDLIM2 expression and resulted in growth arrest. These studies thus provide new mechanistic insights into colon tumorigenesis by identifying a novel tumor suppressor role for PDLIM2.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Munkholm P. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, et al. IKKβ links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 2004;118:285–96. - PubMed
-
- Rogler G, Brand K, Vogl D, et al. Nuclear factor κB is activated in macrophages and epithelial cells of inflamed intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:357–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

