CXCL12-induced chemotaxis is impaired in T cells from patients with ZAP-70-negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 20145264
- PMCID: PMC2864383
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.013995
CXCL12-induced chemotaxis is impaired in T cells from patients with ZAP-70-negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Background: T cells from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia may play an important role in contributing to the onset, sustenance, and exacerbation of the disease by providing survival and proliferative signals to the leukemic clone within lymph nodes and bone marrow.
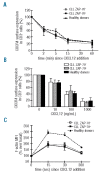
Design and methods: By performing chemotaxis assays towards CXCL12, CCL21 and CCL19, we sought to evaluate the migratory potential of T cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. We next analyzed the chemokine-induced migration of T cells, dividing the chronic lymphocytic leukemia samples according to their expression of the poor prognostic factors CD38 and ZAP-70 in leukemic cells determined by flow cytometry.
Results: We found that T cells from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia are less responsive to CXCL12, CCL21 and CCL19 than T cells from healthy adults despite similar CXCR4 and CCR7 expression. Following separation of the patients into two groups according to ZAP-70 expression, we found that T cells from ZAP-70-negative samples showed significantly less migration towards CXCL12 compared to T cells from ZAP-70-positive samples and that this was not due to defective CXCR4 down-regulation, F-actin polymerization or to a lesser expression of ZAP-70, CD3, CD45, CD38 or CXCR7 on these cells. Interestingly, we found that leukemic cells from ZAP-70-negative samples seem to be responsible for the defective CXCR4 migratory response observed in their T cells.
Conclusions: Impaired migration towards CXCL12 may reduce the access of T cells from ZAP-70-negative patients to lymphoid organs, creating a less favorable microenvironment for leukemic cell survival and proliferation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ZAP-70 expression is associated with enhanced ability to respond to migratory and survival signals in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL).Blood. 2006 May 1;107(9):3584-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1718. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16332969
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells receive RAF-dependent survival signals in response to CXCL12 that are sensitive to inhibition by sorafenib.Blood. 2011 Jan 20;117(3):882-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-282400. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21079155 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through ZAP-70 is required for CXCL12-mediated T-cell transendothelial migration.Blood. 2002 May 1;99(9):3111-8. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.9.3111. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11964272
-
Pitfalls and limitations of ZAP-70 detection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Hematology. 2012 Sep;17(5):268-74. doi: 10.1179/1607845412Y.0000000015. Hematology. 2012. PMID: 22971532 Review.
-
Clinical implications of ZAP-70 expressionin chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2006 Jul 15;70(4):214-7. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.20131. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2006. PMID: 16906580 Review.
Cited by
-
Ibrutinib Does Not Impact CCR7-Mediated Homeostatic Migration in T-Cells from Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 31;14(11):2729. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112729. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681706 Free PMC article.
-
Of Lymph Nodes and CLL Cells: Deciphering the Role of CCR7 in the Pathogenesis of CLL and Understanding Its Potential as Therapeutic Target.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 24;12:662866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.662866. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The kinase inhibitors R406 and GS-9973 impair T cell functions and macrophage-mediated anti-tumor activity of rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017 Apr;66(4):461-473. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1946-y. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28011996 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12 is a costimulator for CD4+ T cell activation and proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Jan;62(1):113-24. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1320-7. Epub 2012 Jul 29. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 22842611 Free PMC article.
-
The cytotoxic activity of Aplidin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is mediated by a direct effect on leukemic cells and an indirect effect on monocyte-derived cells.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Oct;30(5):1830-40. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9740-3. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21887502
References
-
- D’Arena G, Tarnani M, Rumi C, Vaisitti T, Aydin S, De Filippi R, et al. Prognostic significance of combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2007;82(9):787–91. - PubMed
-
- Del Giudice I, Morilla A, Osuji N, Matutes E, Morilla R, Burford A, et al. Zeta-chain associated protein 70 and CD38 combined predict the time to first treatment in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 2005;104(10):2124–32. - PubMed
-
- Schroers R, Griesinger F, Trumper L, Haase D, Kulle B, Klein-Hitpass L, et al. Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression as a predictor of disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2005;19(5):750–8. - PubMed
-
- Hus I, Podhorecka M, Bojarska-Junak A, Rolinski J, Schmitt M, Sieklucka M, et al. The clinical significance of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(4):683–90. - PubMed
-
- Dighiero G, Binet JL. When and how to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(24):1799–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

