High-dose imatinib improves cytogenetic and molecular remissions in patients with pretreated Philadelphia-positive, BCR-ABL-positive chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia: first results from the randomized CELSG phase III CML 11 "ISTAHIT" study
- PMID: 20145273
- PMCID: PMC2878787
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.013979
High-dose imatinib improves cytogenetic and molecular remissions in patients with pretreated Philadelphia-positive, BCR-ABL-positive chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia: first results from the randomized CELSG phase III CML 11 "ISTAHIT" study
Abstract
Background: Imatinib 400 mg/day is the standard treatment for patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Recent reports suggested higher and more rapid cytogenetic and molecular responses with higher doses of imatinib.
Design and methods: In this prospective international, multicenter phase III study, 227 patients with pre-treated Philadelphia chromosome-positive, BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia were randomized to a standard-dose imatinib arm (400 mg/day) or a high-dose imatinib arm (800 mg/day for 6 months followed by 400 mg/day as maintenance therapy). In this planned interim analysis hematologic, cytogenetic and molecular responses as well as toxicity were evaluated.
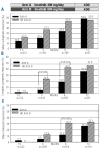
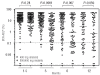
Results: Compared to the standard-dose, high-dose imatinib led to higher rates of major and complete cytogenetic responses at both 3 months (major: 21% versus 37%, P=0.01; complete: 6% versus 25%, P<0.001) and 6 months (major: 34% versus 54%, P=0.009; complete: 20% versus 44%, P<0.001). This was paralleled by a significantly higher major molecular response rate at 6 months in the high-dose imatinib arm (11.8% versus 30.4%; P=0.003). At 12 months, the rates of major cytogenetic response (the primary end-point) were comparable between the two arms (57% versus 59%). In contrast to non-hematologic toxicities, grade 3/4 hematologic toxicities were more common in the high-dose arm. Cumulative complete cytogenetic response rates were higher in patients without dose reduction in the high-dose arm (61%) than in the patients with no dose reduction in the standard-dose arm (36%) (P=0.014).
Conclusions: This is the first randomized phase III trial in patients with pre-treated chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia demonstrating improvements in major cytogenetic response, complete cytogenetic response and major molecular response rates with high-dose imatinib therapy (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00327262).
Figures

References
-
- O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(11):994–1004. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(23):2408–17. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Goldman JM, et al. International randomized study of interferon versus STI57 (IRIS) 7-year follow-up: sustained survival, low rate of transformation and increased rate of major molecular response (MMR) in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with imatinib (IM) Blood. 2008;112(11):186a.
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(14):1031–7. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, O’Brien S, Giles F, Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S, et al. Dose escalation of imatinib mesylate can overcome resistance to standard-dose therapy in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2003;101(2):473–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

