Totally automatic definition of renal regions of interest from 99mTc-MAG3 renograms: validation in patients with normal kidneys and in patients with suspected renal obstruction
- PMID: 20145580
- PMCID: PMC2884994
- DOI: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e3283362aa3
Totally automatic definition of renal regions of interest from 99mTc-MAG3 renograms: validation in patients with normal kidneys and in patients with suspected renal obstruction
Abstract
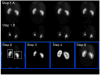
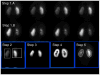
Introduction: An image-processing algorithm (AUTOROI) has been developed to totally automatically (or with manual assistance) detect whole-kidney contours and generate renal regions of interest (ROI) for the extraction of the quantitative measurements used in the interpretation of Tc-mercaptoacetyltriglycine (Tc-MAG3) renograms.
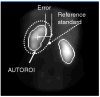
Methods: The 18-20th min dynamic frames post-MAG3 injection were used to automatically define boxes surrounding each kidney, which were then transposed to an early composite image for interpolative and directional background subtraction. Sobel operator and unsharp masking were applied for edge enhancement, and the resulting image histograms were equalized to better define poorly functioning kidneys. AUTOROI searched radially from the center of mass to define each kidney's ROI coordinates. AUTOROI was validated using MAG3 studies from 79 patients referred for suspected obstruction (79 left, 77 right kidneys) and 19 kidney donors with normal kidney function and no obstruction. Renal ROIs were manually defined by a nuclear medicine technologist with 20+ years of experience (reference standard) and an American Board of Nuclear Medicine certified physician. AUTOROI and physician ROIs were automatically compared with the reference standard to determine the border definition error.
Results: AUTOROI totally automatically detected the renal borders in 89% (172 of 194) of the kidneys from the entire group of 98 patients. The 22 kidneys missed automatically were subsequently detected with the assistance of a single manually placed fiducial point demarcating the liver/kidney boundary. These 22 kidneys were shown to be associated with markedly reduced MAG3 clearance. The mean error of AUTOROI for all 194 kidneys was 6.66+/-3.77 and 7.31+/-4.52 mm for the left and right kidney, respectively. The physician's error was 6.78+/-2.42 and 6.65+/-2.05 mm for the left and right kidney, respectively. This error difference between AUTOROI and the physician was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: AUTOROI provides an objective and promising approach to automated renal ROI detection.
Figures

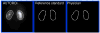

Comment in
-
Automatic definition of renal regions of interest.Nucl Med Commun. 2011 May;32(5):419-20; author reply 420-1. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e3283406dea. Nucl Med Commun. 2011. PMID: 21467873 No abstract available.
References
-
- Taylor A, Jr, Corrigan PL, Galt J, et al. Measuring technetium-99m-MAG3 clearance with an improved camera-based method. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1689–1695. - PubMed
-
- Garcia EV, Taylor A, Halkar R, Folks R, Krishnan M, Dubovsky E. RENEX: An Expert System for the Interpretation of 99mTc-MAG3 Scans to Detect Renal Obstruction. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:320–329. - PubMed
-
- White D, Houston A, Sampson W, Wilkins GP. Intra- and interoperator variations in region-of-interest drawing and their effect on the measurement of glomerular filtration rates. Clinical Nuclear Medicine. 1999;3:24. 177–181. - PubMed
-
- Pavel DG, Orellana P, Olea E. Factor analysis of Tc-DTPA and I-hippuran radionuclide renal studies in nephro-urology. Eur J Nucl Med. 1989;15:514.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

