TLR9 and IRF3 cooperate to induce a systemic inflammatory response in mice injected with liposome:DNA
- PMID: 20145605
- PMCID: PMC2862521
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.1
TLR9 and IRF3 cooperate to induce a systemic inflammatory response in mice injected with liposome:DNA
Abstract
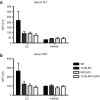
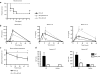
Liposome:DNA is a promising gene therapy vector. However, this vector can elicit a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Prior reports indicate that liposome:DNA vectors activate Toll-like receptor (TLR)9. We hypothesized that liposome:DNA vectors also activate the cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway, which signals via interferon (IFN) regulatory factor (IRF)3. To test this, we treated dendritic cells (DCs) with liposome:DNA in vitro and found that IRF3 was phosphorylated independent of TLR9. To test the contribution of this pathway in vivo, we injected a liposome:DNA vector into wild-type (WT), TLR9-knockout (KO), IRF3-KO, and TLR9-IRF3-double-KO (DKO) mice. WT mice exhibited a systemic inflammatory response, evidenced by elevations in serum cytokines, serum enzyme changes indicating organ damage, hypothermia, and mortality. The cytokine response was reduced in TLR9-KO, IRF3-KO, and TLR9-IRF3-DKO mice and all three groups survived. We found that IFN-gamma-KO mice that receive liposome:DNA had a reduced cytokine response and 100% survival. CD11c(+) and NK1.1(+) cells produced IFN-gamma and depleting CD11c(+) cells reduced the cytokine response in mice injected with liposome:DNA. These findings may facilitate the development of immunologically inert gene therapy vectors and may provide general insight into the mechanisms of SIRS.
Figures

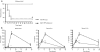

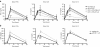
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the type of liposome involving cytokine production induced by non-CpG Lipoplex in macrophages.Mol Pharm. 2010 Apr 5;7(2):533-42. doi: 10.1021/mp900247d. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20047296
-
Dietary deoxynucleic acid induces type 2 T-helper immune response through toll-like receptor 9 in mice.Eur J Nutr. 2011 Sep;50(6):421-6. doi: 10.1007/s00394-010-0153-4. Epub 2010 Dec 4. Eur J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21132311
-
Interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 protects mice from uterine horn pathology during Chlamydia muridarum genital infection.Infect Immun. 2011 Oct;79(10):3922-33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00140-11. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21788382 Free PMC article.
-
IRF-3, IRF-5, and IRF-7 coordinately regulate the type I IFN response in myeloid dendritic cells downstream of MAVS signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003118. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003118. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23300459 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of TLR9 by incorporated pDNA within PEG-coated lipoplex enhances anti-PEG IgM production.Gene Ther. 2014 Jun;21(6):593-8. doi: 10.1038/gt.2014.32. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 24694537
Cited by
-
The Role of Nucleic Acid Sensing in Controlling Microbial and Autoimmune Disorders.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;345:35-136. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30904196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible role of TLR4 and TLR9 SNPs in protection against congenital toxoplasmosis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Oct;34(10):2121-9. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2461-3. Epub 2015 Aug 9. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26254559 Free PMC article.
-
IRF3 contributes to sepsis pathogenesis in the mouse cecal ligation and puncture model.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Dec;92(6):1261-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0312138. Epub 2012 Oct 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 23048204 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of endosomal members of toll-like receptor family abrogates wound healing in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Int Wound J. 2016 Oct;13(5):927-35. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12411. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Int Wound J. 2016. PMID: 25586463 Free PMC article.
-
IRF3 Signaling within the Mouse Stroma Influences Sepsis Pathogenesis.J Immunol. 2021 Jan 15;206(2):398-409. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900217. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33239421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scheule RK, St George JA, Bagley RG, Marshall J, Kaplan JM, Akita GY, et al. Basis of pulmonary toxicity associated with cationic lipid-mediated gene transfer to the mammalian lung. Hum Gene Ther. 1997;8:689–707. - PubMed
-
- McMahon JM, Wells KE, Bamfo JE, Cartwright MA., and , Wells DJ. Inflammatory responses following direct injection of plasmid DNA into skeletal muscle. Gene Ther. 1998;5:1283–1290. - PubMed
-
- Freimark BD, Blezinger HP, Florack VJ, Nordstrom JL, Long SD, Deshpande DS, et al. Cationic lipids enhance cytokine and cell influx levels in the lung following administration of plasmid: cationic lipid complexes. J Immunol. 1998;160:4580–4586. - PubMed
-
- Yew NS, Wang KX, Przybylska M, Bagley RG, Stedman M, Marshall J, et al. Contribution of plasmid DNA to inflammation in the lung after administration of cationic lipid:pDNA complexes. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10:223–234. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Wu SP, Whitmore M, Loeffert EJ, Wang L, Watkins SC, et al. Effect of immune response on gene transfer to the lung via systemic administration of cationic lipidic vectors. Am J Physiol. 1999;276 5 Pt 1:L796–L804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

