The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and the lung
- PMID: 20145712
- PMCID: PMC2817378
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/917108
The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and the lung
Abstract
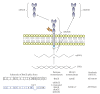
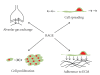
The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell surface molecules. As a pattern-recognition receptor capable of binding a diverse range of ligands, it is typically expressed at low levels under normal physiological conditions in the majority of tissues. In contrast, the lung exhibits high basal level expression of RAGE localised primarily in alveolar type I (ATI) cells, suggesting a potentially important role for the receptor in maintaining lung homeostasis. Indeed, disruption of RAGE levels has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of pulmonary disorders including cancer and fibrosis. Furthermore, its soluble isoforms, sRAGE, which act as decoy receptors, have been shown to be a useful marker of ATI cell injury. Whilst RAGE undoubtedly plays an important role in the biology of the lung, it remains unclear as to the exact nature of this contribution under both physiological and pathological conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, et al. Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation end products of proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267(21):14998–15004. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt AM, Vianna M, Gerlach M, et al. Isolation and characterization of two binding proteins for advanced glycosylation end products from bovine lung which are present on the endothelial cell surface. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267(21):14987–14997. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Wautier J-L, Stern D. Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products: a mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis. Circulation Research. 1999;84(5):489–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

