Dynamic expression of a LEF-EGFP Wnt reporter in mouse development and cancer
- PMID: 20146356
- PMCID: PMC3399184
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.20604
Dynamic expression of a LEF-EGFP Wnt reporter in mouse development and cancer
Abstract
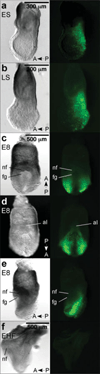
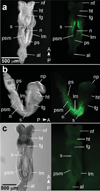
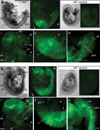
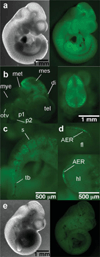
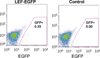
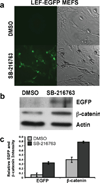
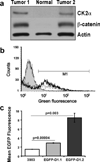
We have characterized a transgenic mouse line in which enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) is expressed under the control of multimerized LEF-1 responsive elements. In embryos, EGFP was detected in known sites of Wnt activation, including the primitive streak, mesoderm, neural tube, somites, heart, limb buds, mammary placodes, and whisker follicles. In vitro cultured transgenic embryonic fibroblasts upregulated EGFP expression in response to activation of Wnt signaling by GSK3beta inhibition. Mammary tumor cell lines derived from female LEF-EGFP transgenic mice treated with the carcinogen 7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) also express EGFP. Thus, this transgenic line is useful for ex vivo and in vitro studies of Wnt signaling in development and cancer.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold SJ, Stappert J, Bauer A, Kispert A, Herrmann BG, Kemler R. Brachyury is a target gene of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mech Dev. 2000;91:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Barker N. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;468:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Barolo S. Transgenic Wnt/TCF pathway reporters: All you need is Lef? Oncogene. 2006;25:7505–7511. - PubMed
-
- Bastidas F, De Calisto J, Mayor R. Identification of neural crest competence territory: Role of Wnt signaling. Dev Dyn. 2004;229:109–117. - PubMed
-
- Boras-Granic K, Chang H, Grosschedl R, Hamel PA. Lef1 is required for the transition of Wnt signaling from mesenchymal to epithelial cells in the mouse embryonic mammary gland. Dev Biol. 2006;295:219–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

