Epilepsy in the elderly
- PMID: 20146700
- PMCID: PMC4900895
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05113.x
Epilepsy in the elderly
Abstract
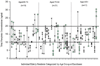
The elderly, often defined as those 65 years or older, are the most rapidly growing segment of the population, and onset of epilepsy is higher in this age group than in any other. This paper reviews recent developments, including a new proposed definition of epilepsy, a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease that exhibits complex partial seizures, evidence that the highest incidence of epilepsy may occur after admission to a nursing home, a challenge to the vitamin D hypothesis of osteoporosis associated with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), evidence that the genetic complement of hepatic isoenzymes is more predictive of metabolic rate than age, and data showing that there is considerable variability in serum levels of AEDs in many nursing home residents during constant dosing conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Administration on Aging. Washington, DC: 2005.
-
- Hauser W, Hesdorffer D. Epilepsy, Frequency, Causes and Consequences. New York, NY: Demos Publications; 1990.
-
- Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Rocca WA. Mayo Clin Proc. 1996;71:576–586. - PubMed
-
- Epilepsy Foundation of America. Landover MD: 1999.
-
- de la Court A, Breteler MM, Meinardi H, Hauser WA, Hofman A. Epilepsia. 1996;37:141–147. - PubMed

