New insights into T cell biology and T cell-directed therapy for autoimmunity, inflammation, and immunosuppression
- PMID: 20146712
- PMCID: PMC2950114
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05124.x
New insights into T cell biology and T cell-directed therapy for autoimmunity, inflammation, and immunosuppression
Abstract
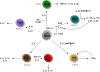
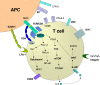
T cell-directed therapies have become mainstays in the management of various autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation. The understanding of T cell biology has expanded greatly since the development of most agents currently in use. Here we discuss important recent discoveries pertaining to T helper cell differentiation, lineage commitment, and function. Within this context, we examine existing T cell-directed therapies, including new agents being evaluated in clinical and preclinical studies. We also use recent findings to speculate on novel targets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autoimmunity: present-day concepts and future prospects.Curr Probl Pediatr. 1991 Jul;21(6):253-8. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(91)90017-f. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1991. PMID: 1914513 Review. No abstract available.
-
Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin.N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 6;345(10):747-55. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra993360. N Engl J Med. 2001. PMID: 11547745 Review. No abstract available.
-
A CD8+ T cell transcription signature predicts prognosis in autoimmune disease.Nat Med. 2010 May;16(5):586-91, 1p following 591. doi: 10.1038/nm.2130. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20400961 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive therapy of autoimmune diseases.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 May;14(5):213-6. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90211-2. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993. PMID: 8212318 Review.
-
An Overview of Organ-Specific Autoimmune Diseases Including Immunotherapy.Immunol Invest. 2015;44(8):803-16. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2015.1099409. Immunol Invest. 2015. PMID: 26575465 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular miR-2909 RNomics governs the genes that ensure immune checkpoint regulation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Jan;451(1-2):37-42. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3390-0. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 29926320
-
Targeted suppression of autoreactive CD8+ T-cell activation using blocking anti-CD8 antibodies.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 17;6:35332. doi: 10.1038/srep35332. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27748447 Free PMC article.
-
The yin and yang of protein kinase C-theta (PKCθ): a novel drug target for selective immunosuppression.Adv Pharmacol. 2013;66:267-312. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-404717-4.00006-8. Adv Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23433459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of the immunosuppressive interleukin-35 in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2019 Apr;120(9):903-912. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0444-3. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Br J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30956278 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Proliferative Effect of Allium senescens L. Extract in Human T-Cell Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells.Molecules. 2020 Dec 23;26(1):35. doi: 10.3390/molecules26010035. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33374788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong C, Flavell RA. Th1 and Th2 cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001;8:47–51. - PubMed
-
- Jankovic D, Sher A, Yap G. Th1/Th2 effector choice in parasitic infection: decision making by committee. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:403–409. - PubMed
-
- Mowen KA, Glimcher LH. Signaling pathways in Th2 development. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:203–222. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KM. Fate vs choice: the immune system reloaded. Immunol Res. 2005;32:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, et al. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:713–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

