Th1 and Th17 cells: adversaries and collaborators
- PMID: 20146717
- PMCID: PMC2914500
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05133.x
Th1 and Th17 cells: adversaries and collaborators
Abstract
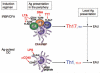
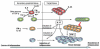
Autoreactive effector CD4+ T cells have been associated with the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders. Early studies implicated the interferon (IFN)-gamma-producing T helper (Th)1 subset of CD4+ cells as the causal agents in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity. However, further studies have suggested a more complex story. In models thought to be driven by Th1 cells, mice lacking the hallmark Th1 cytokine IFN-gamma were not protected but tended to have enhanced susceptibility to disease. Identification of the IL-17-producing CD4+ effector cell lineage (Th17) has helped shed light on this issue. Th17 effector cells are induced in parallel to Th1, and, like Th1, polarized Th17 cells have the capacity to cause inflammation and autoimmune disease. This, together with the finding that deficiency of the Th17-related cytokine IL-23 but not the Th1-related cytokine IL-12 causes resistance, led to the notion that Th17 cells are the chief contributors to autoimmune tissue inflammation. Nevertheless, mice lacking IL-17 are not protected from disease and display elevated numbers of IFN-gamma-producing CD4+ T cells, and, in some cases, lack of IFN-gamma does confer resistance. Recent studies report overlapping as well as differential roles of these cells in tissue inflammation, which suggests the existence of a more complex relationship between these two effector T-cell subsets than has hitherto been suspected. This review will attempt to bring together current information regarding interaction, balance, and collaborative potential between the Th1 and Th17 effector lineages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Th17 cells comprise heterogeneous subsets including IFN-gamma-producing cells with distinct properties from the Th1 lineage.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):679-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000366. Epub 2010 May 28. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20511558
-
Phenotype switching by inflammation-inducing polarized Th17 cells, but not by Th1 cells.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 15;181(10):7205-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7205. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18981142 Free PMC article.
-
IL-7/IL-7 Receptor Signaling Differentially Affects Effector CD4+ T Cell Subsets Involved in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):1974-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403135. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26223651 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-γ and IL-17: the two faces of T-cell pathology in giant cell arteritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Jan;23(1):43-9. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833ee946. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 20827207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High salt diet alleviates disease severity in native experimental autoimmune uveitis.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 May 31;4:1370374. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1370374. eCollection 2024. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38984146 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Two Major Toxoplasma Gondii Virulence Factors (ROP16 and ROP18) on the Immune Response of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells to Human Toxoplasmosis Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Dec 4;9:413. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00413. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31867288 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A, systemic T-cells, and the eye: Focus on degenerative retinal disease.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 18;9:914457. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.914457. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35923205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in serum immunomolecules during antibiotic therapy for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Apr;176(1):93-101. doi: 10.1111/cei.12253. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24354934 Free PMC article.
-
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates cytokine production induced by Candida albicans: impact of seasonal variation of immune responses.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jan 1;203(1):122-30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq008. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21148505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
-
- Ferber IA, et al. Mice with a disrupted IFN-gamma gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) J. Immunol. 1996;156:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Jones LS, et al. IFN-gamma-deficient mice develop experimental autoimmune uveitis in the context of a deviant effector response. J. Immunol. 1997;158:5997–6005. - PubMed
-
- Matthys P, et al. Anti-IL-12 antibody prevents the development and progression of collagen-induced arthritis in IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998;28:2143–2151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

