Using machine learning to speed up manual image annotation: application to a 3D imaging protocol for measuring single cell gene expression in the developing C. elegans embryo
- PMID: 20146825
- PMCID: PMC2838868
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-84
Using machine learning to speed up manual image annotation: application to a 3D imaging protocol for measuring single cell gene expression in the developing C. elegans embryo
Abstract
Background: Image analysis is an essential component in many biological experiments that study gene expression, cell cycle progression, and protein localization. A protocol for tracking the expression of individual C. elegans genes was developed that collects image samples of a developing embryo by 3-D time lapse microscopy. In this protocol, a program called StarryNite performs the automatic recognition of fluorescently labeled cells and traces their lineage. However, due to the amount of noise present in the data and due to the challenges introduced by increasing number of cells in later stages of development, this program is not error free. In the current version, the error correction (i.e., editing) is performed manually using a graphical interface tool named AceTree, which is specifically developed for this task. For a single experiment, this manual annotation task takes several hours.
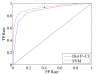
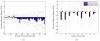
Results: In this paper, we reduce the time required to correct errors made by StarryNite. We target one of the most frequent error types (movements annotated as divisions) and train a support vector machine (SVM) classifier to decide whether a division call made by StarryNite is correct or not. We show, via cross-validation experiments on several benchmark data sets, that the SVM successfully identifies this type of error significantly. A new version of StarryNite that includes the trained SVM classifier is available at http://starrynite.sourceforge.net.
Conclusions: We demonstrate the utility of a machine learning approach to error annotation for StarryNite. In the process, we also provide some general methodologies for developing and validating a classifier with respect to a given pattern recognition task.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The lineaging of fluorescently-labeled Caenorhabditis elegans embryos with StarryNite and AceTree.Nat Protoc. 2006;1(3):1468-76. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.222. Nat Protoc. 2006. PMID: 17406437
-
AceTree: a tool for visual analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans embryogenesis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jun 1;7:275. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-275. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16740163 Free PMC article.
-
Automated tracking and analysis of centrosomes in early Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 15;26(12):i13-20. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq190. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20529897 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle timing regulation during asynchronous divisions of the early C. elegans embryo.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Oct 1;337(2):243-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 26213213 Review.
-
Nutritional control of postembryonic development progression and arrest in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Genet. 2021;107:33-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Adv Genet. 2021. PMID: 33641748 Review.
Cited by
-
Delineating the mechanisms and design principles of Caenorhabditis elegans embryogenesis using in toto high-resolution imaging data and computational modeling.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Aug 19;20:5500-5515. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.024. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36284714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel cell nuclei segmentation method for 3D C. elegans embryonic time-lapse images.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Nov 19;14:328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-328. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 24252066 Free PMC article.
-
A semi-local neighborhood-based framework for probabilistic cell lineage tracing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Jun 25;15:217. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-217. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24964866 Free PMC article.
-
The early bird catches the worm: new technologies for the Caenorhabditis elegans toolkit.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Oct 4;12(11):793-801. doi: 10.1038/nrg3050. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21969037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization and correction of automated segmentation, tracking and lineaging from 5-D stem cell image sequences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Oct 3;15(1):328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-328. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25281197 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

