Leukotriene B4, administered via intracerebroventricular injection, attenuates the antigen-induced asthmatic response in sensitized guinea pigs
- PMID: 20146826
- PMCID: PMC2834663
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-12
Leukotriene B4, administered via intracerebroventricular injection, attenuates the antigen-induced asthmatic response in sensitized guinea pigs
Abstract
Background: Despite intensive studies focused on the pathophysiology of asthmatic inflammation, little is known about how cross-talk between neuroendocrine and immune systems regulates the inflammatory response during an asthmatic attack. We recently showed corresponding changes of cytokines and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) in brain and lung tissues of antigen-challenged asthmatic rats. Here, we investigated how LTB4 interacts with the neuroendocrine-immune system in regulating antigen-induced asthmatic responses in sensitized guinea pigs.
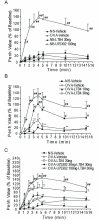
Methods: Ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs were challenged by inhalation of antigen. Vehicle, LTB4 or U75302 (a selective LTB4 BLT1 receptor inhibitor) was given via intracerebroventricular injection (i.c.v.) 30 min before challenge. Airway contraction response was evaluated using Penh values before and after antigen challenge. The inflammatory response in lung tissue was evaluated 24 h after challenge. The LTB4 content of lung and brain homogenate preparations was detected by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). Plasma levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and corticosterone (CORT) were measured using ELISA kits.
Results: Antigen challenge impaired pulmonary function and increased inflammatory cell infiltration in lung tissue. These responses could be significantly suppressed by LTB4, 30 ng i.c.v., in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. LTB4 content of lung and brain homogenates from antigen-challenged guinea pigs was significantly increased. In addition, administration of LTB4 via i.c.v. markedly increased CORT and ACTH level in plasma before antigen challenge, and there were further increases in CORT and ACTH levels in plasma after antigen challenge. U75302, 100 ng i.c.v., completely blocked the effects of LTB4. In addition, U75302, 100 ng via i.c.v. injection, markedly decreased LTB4 content in lung homogenates, but not in brain homogenates.
Conclusions: Increased LTB4 levels in brain during asthmatic attacks down-regulates airway contraction response and inflammation through the BLT1 receptor. Stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by LTB4 may result in an increase in systemic glucocorticoids which, in turn, would feed back to suppress the asthmatic response.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intracerebroventricular injection of leukotriene B4 attenuates antigen-induced asthmatic response via BLT1 receptor stimulating HPA-axis in sensitized rats.Respir Res. 2010 Apr 20;11(1):39. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-39. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 20403205 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the selective leukotriene B4 antagonist U-75302 on antigen-induced bronchopulmonary eosinophilia in sensitized guinea pigs.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1712-6. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1712. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989. PMID: 2557787
-
Coincidental increase of leukotriene B4 between cerebral cortex and lung tissue of sensitized rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003 Oct;24(10):1039-44. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003. PMID: 14531949
-
Biological activity of leukotriene B4 analogs: inhibition of guinea pig eosinophil migration in vitro by the 2,6-disubstituted pyridine analogs U-75,302 and U-75,485.Prostaglandins. 1991 Sep;42(3):211-24. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(91)90111-r. Prostaglandins. 1991. PMID: 1664113
-
The Role of LTB4 in Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance Development: An Overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 22;13:848006. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.848006. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35392132 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Generation of Bioactive Oxylipins from Exogenously Added Arachidonic, Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acid in Primary Human Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells.Lipids. 2016 May;51(5):591-9. doi: 10.1007/s11745-015-4074-0. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 26439837
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

