Role of the hypothalamic PVN in the regulation of renal sympathetic nerve activity and blood flow during hyperthermia and in heart failure
- PMID: 20147365
- PMCID: PMC2853311
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00734.2009
Role of the hypothalamic PVN in the regulation of renal sympathetic nerve activity and blood flow during hyperthermia and in heart failure
Abstract
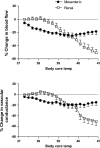
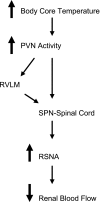
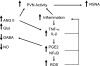
The hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus is a key integrative area in the brain involved in influencing sympathetic nerve activity and in the release of hormones or releasing factors that contribute to regulating body fluid homeostasis and endocrine function. The endocrine and hormonal regulatory function of the paraventricular nucleus is well studied, but the regulation of sympathetic nerve activity and blood flow by this region is less clear. Here we review the critical role of the paraventricular nucleus in regulating renal blood blow during hyperthermia and the evidence pointing to an important pathophysiological role of the paraventricular nucleus in the elevated renal sympathetic nerve activity that is a characteristic of heart failure.
Figures
References
-
- Akama H, Mcgrath BP, Badoer E. Volume expansion fails to normally activate neural pathways in the brain of conscious rabbits with heart failure. J Autonom Nerv Syst 73: 54–62, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bachtell RK, Tsivkovskaia NO, Ryabinin AE. Identification of temperature-sensitive neural circuits in mice using c-Fos expression mapping. Brain Res 960: 157–164, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Badoer E. Cardiovascular role of parvocellular neurones in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. News Physiol Sci 11: 43–47, 1996
-
- Badoer E, Moguilevski V, Mcgrath BP. Cardiac afferents play the dominant role in renal nerve inhibition elicited by volume expansion in the rabbit. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 274: R383–R388, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

