Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins H/L bind to cells independently of {alpha}V{beta}3 integrin and inhibit virus entry, and their constitutive expression restricts infection
- PMID: 20147400
- PMCID: PMC2849490
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02502-09
Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins H/L bind to cells independently of {alpha}V{beta}3 integrin and inhibit virus entry, and their constitutive expression restricts infection
Abstract
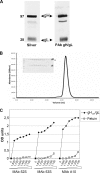
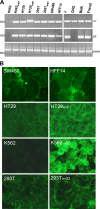
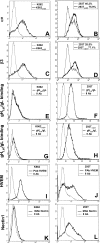
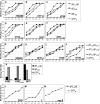
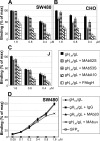
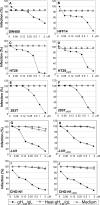
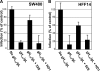
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) fusion with cells requires the gD, gB, and gH/gL glycoprotein quartet. gD serves as a receptor binding glycoprotein. gB and gH/gL execute fusion in an as-yet-unclear manner. To better understand the role of gH/gL in HSV entry, we produced a soluble version of gH/gL carrying a One-STrEP tag (gH(t.st)/gL). Previous findings implicated integrins as possible ligands to gH/gL (C. Parry et al., J. Gen. Virol. 86:7-10, 2005). We report that (i) gH(t.st)/gL bound a number of cells in a dose-dependent manner at concentrations similar to those required for the binding of soluble gB or gD. (ii) gH(t.st)/gL inhibited HSV entry at the same concentrations required for binding. It also inhibited cell-cell fusion in transfected cells. (iii) The absence of beta3 integrin did not prevent the binding of gH(t.st)/gL to CHO cells and infection inhibition. Conversely, integrin-negative K562 cells did not acquire the ability to bind gH(t.st)/gL when hyperexpressing alphaVbeta3 integrin. (iv) Constitutive expression of wild-type gH/gL (wt-gH/gL) restricted infection in all of the cell lines tested, a behavior typical of glycoproteins which bind cellular receptors. The extent of restriction broadly paralleled the efficiency of gH/gL transfection. RGD motif mutant gH/gL could not be differentiated from wt-gH with respect to restriction of infection. Cumulatively, the present results provide several lines of evidence that HSV gH/gL interacts with a cell surface cognate protein(s), that this protein is not necessarily an alphaVbeta3 integrin, and that this interaction is required for the process of virus entry/fusion.
Figures
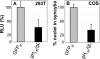
Similar articles
-
αvβ6- and αvβ8-integrins serve as interchangeable receptors for HSV gH/gL to promote endocytosis and activation of membrane fusion.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(12):e1003806. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003806. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24367260 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of herpes simplex virus gB-induced cell-cell fusion by mutant forms of gH/gL in the absence of gD and cellular receptors.mBio. 2013 Feb 26;4(2):e00046-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00046-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23443004 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk among the glycoproteins involved in herpes simplex virus entry and fusion: the interaction between gB and gH/gL does not necessarily require gD.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(20):10752-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01287-09. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19656900 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of HSV Glycoproteins in Mediating Cell Entry.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896660 Review.
-
Viral and cellular contributions to herpes simplex virus entry into the cell.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Feb;2(1):28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.12.001. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22440963 Review.
Cited by
-
Reevaluating herpes simplex virus hemifusion.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(22):11814-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01615-10. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20844038 Free PMC article.
-
{alpha}V{beta}3-integrin routes herpes simplex virus to an entry pathway dependent on cholesterol-rich lipid rafts and dynamin2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 21;107(51):22260-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014923108. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21135248 Free PMC article.
-
Fusing structure and function: a structural view of the herpesvirus entry machinery.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 May;9(5):369-81. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2548. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21478902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of glycoprotein H of equine herpesviruses 1 and 4 (EHV-1 and EHV-4) in cellular host range and integrin binding.Vet Res. 2012 Aug 21;43(1):61. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-43-61. Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 22909178 Free PMC article.
-
αvβ6- and αvβ8-integrins serve as interchangeable receptors for HSV gH/gL to promote endocytosis and activation of membrane fusion.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(12):e1003806. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003806. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24367260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

