Ablation of the complementarity-determining region H3 apex of the anti-HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody 2F5 abrogates neutralizing capacity without affecting core epitope binding
- PMID: 20147404
- PMCID: PMC2863773
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02357-09
Ablation of the complementarity-determining region H3 apex of the anti-HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody 2F5 abrogates neutralizing capacity without affecting core epitope binding
Abstract
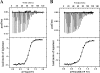
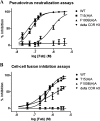
The identification and characterization of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) against HIV-1 has formed a major research focus, with the ultimate goal to help in the design of an effective AIDS vaccine. One of these bnAbs, 2F5, has been extensively characterized, and residues at the apex of its unusually long complementarity-determining region (CDR) H3 loop have been shown to be crucial for neutralization. Structural studies, however, have revealed that the (100)TLFGVPI(100F) apex residues of the CDR H3 loop do not interact directly with residues of its core gp41 epitope. In an attempt to gain better insight into the functional role of this element, we have recombinantly expressed native 2F5 Fab and two mutants in which either the apical Phe100B(H) residue was changed to an alanine or the CDR H3 residues (100)TLFGVPI(100F) were replaced by a Ser-Gly dipeptide linker. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) and competitive-binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) rendered strikingly similar affinity constants (K(d) [dissociation constant] of approximately 20 nM) for linear peptide epitope binding by 2F5 Fabs, independent of the presence or absence of the apex residues. Ablation of the CDR H3 apex residues, however, abolished the cell-cell fusion inhibition and pseudovirus neutralization capacities of 2F5 Fab. We report competitive ELISA data that suggest a role of 2F5 CDR H3 apex residues in mediating weak hydrophobic interactions with residues located at the C terminus of the gp41 membrane proximal external region and/or membrane components in the context of core epitope binding. The present data therefore imply an extended 2F5 paratope that includes weak secondary interactions that are crucial for neutralization of Env-mediated fusion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The long third complementarity-determining region of the heavy chain is important in the activity of the broadly neutralizing anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibody 2F5.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(6):3155-61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.6.3155-3161.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14990736 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of anti-HIV type 1 antibody 2F5 with phospholipid bilayers and its relevance for the mechanism of virus neutralization.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2011 Aug;27(8):863-76. doi: 10.1089/AID.2010.0265. Epub 2011 Jan 15. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2011. PMID: 21142698
-
Structural and Thermodynamic Basis of Epitope Binding by Neutralizing and Nonneutralizing Forms of the Anti-HIV-1 Antibody 4E10.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):11975-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01793-15. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26378169 Free PMC article.
-
Progress towards the development of a HIV-1 gp41-directed vaccine.Curr HIV Res. 2004 Apr;2(2):193-204. doi: 10.2174/1570162043484933. Curr HIV Res. 2004. PMID: 15078183 Review.
-
Antigp41 membrane proximal external region antibodies and the art of using the membrane for neutralization.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017 May;12(3):250-256. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000364. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28422789 Review.
Cited by
-
Rational design of vaccines to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2011 Sep;1(1):a007278. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007278. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2011. PMID: 22229123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral Membrane Interactions Boost the Engagement by an Anti-HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibody.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 31;292(13):5571-5583. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.775429. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28213514 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody mechanics on a membrane-bound HIV segment essential for GP41-targeted viral neutralization.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Oct 16;18(11):1235-43. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2154. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22002224 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and immunogenicity of a peptide vaccine, including the complete HIV-1 gp41 2F5 epitope: implications for antibody recognition mechanism and immunogen design.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6565-6580. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527747. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24429284 Free PMC article.
-
Computational design of protein antigens that interact with the CDR H3 loop of HIV broadly neutralizing antibody 2F5.Proteins. 2014 Oct;82(10):2770-82. doi: 10.1002/prot.24641. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Proteins. 2014. PMID: 25043744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff, M. D., P. J. Magelhaes, and S. J. Ram. 2004. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 11:36-42.
-
- Alam, S. M., M. McAdams, D. Boren, M. Rak, R. M. Scearce, F. Gao, Z. T. Camacho, D. Gewirth, G. Kelsoe, P. Chen, and B. F. Haynes. 2007. The role of antibody polyspecificity and lipid reactivity in binding of broadly neutralizing anti-HIV-1 envelope human monoclonal antibodies 2F5 and 4E10 to glycoprotein 41 membrane proximal envelope epitopes. J. Immunol. 178:4424-4435. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold, G. F., P. K. Velasco, A. K. Holmes, T. Wrin, S. C. Geisler, P. Phung, Y. Tian, D. A. Resnick, X. Ma, T. M. Mariano, C. J. Petropoulos, J. W. Taylor, H. Katinger, and E. Arnold. 2009. Broad neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) elicited from human rhinoviruses that display the HIV-1 gp41 ELDKWA epitope. J. Virol. 83:5087-5100. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

