Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine strains expressing a nontoxic Shiga-like toxin 2 derivative induce partial protective immunity to the toxin expressed by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20147499
- PMCID: PMC2849334
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00495-09
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine strains expressing a nontoxic Shiga-like toxin 2 derivative induce partial protective immunity to the toxin expressed by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
Abstract
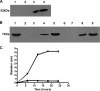
Shiga-like toxin 2 (Stx2)-producing enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (referred to as EHEC or STEC) strains are the primary etiologic agents of hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS), which leads to renal failure and high mortality rates. Expression of Stx2 is the most relevant virulence-associated factor of EHEC strains, and toxin neutralization by antigen-specific serum antibodies represents the main target for both preventive and therapeutic anti-HUS approaches. In the present report, we describe two Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium aroA vaccine strains expressing a nontoxic plasmid-encoded derivative of Stx2 (Stx2DeltaAB) containing the complete nontoxic A2 subunit and the receptor binding B subunit. The two S. Typhimurium strains differ in the expression of flagellin, the structural subunit of the flagellar shaft, which exerts strong adjuvant effects. The vaccine strains expressed Stx2DeltaAB, either cell bound or secreted into the extracellular environment, and showed enhanced mouse gut colonization and high plasmid stability under both in vitro and in vivo conditions. Oral immunization of mice with three doses of the S. Typhimurium vaccine strains elicited serum anti-Stx2B (IgG) antibodies that neutralized the toxic effects of the native toxin under in vitro conditions (Vero cells) and conferred partial protection under in vivo conditions. No significant differences with respect to gut colonization or the induction of antigen-specific antibody responses were detected in mice vaccinated with flagellated versus nonflagellated bacterial strains. The present results indicate that expression of Stx2DeltaAB by attenuated S. Typhimurium strains is an alternative vaccine approach for HUS control, but additional improvements in the immunogenicity of Stx2 toxoids are still required.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in the development of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli vaccines using murine models of infection.Vaccine. 2013 Jul 11;31(32):3229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 22. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23707170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli trivalent recombinant vaccine containing EspA, intimin and Stx2 induces strong humoral immune response and confers protection in mice.Microbes Infect. 2009 Sep;11(10-11):835-41. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.04.024. Epub 2009 May 7. Microbes Infect. 2009. PMID: 19427397
-
A Poly-N-acetylglucosamine-Shiga toxin broad-spectrum conjugate vaccine for Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli.mBio. 2014 Mar 25;5(2):e00974-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00974-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24667709 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA vaccine encoding the enterohemorragic Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin 2 A2 and B subunits confers protective immunity to Shiga toxin challenge in the murine model.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 May;16(5):712-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00328-08. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19176691 Free PMC article.
-
Shiga Toxin: Emerging Producer Strains, Prophylactic Approaches, and Application in Cancer Therapy.J Cancer Prev. 2024 Dec 30;29(4):120-128. doi: 10.15430/JCP.24.010. J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39790227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the development of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli vaccines using murine models of infection.Vaccine. 2013 Jul 11;31(32):3229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 22. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23707170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-multilamellar lipid vesicles (NMVs) enhance protective antibody responses against Shiga toxin (Stx2a) produced by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains (EHEC).Braz J Microbiol. 2019 Jan;50(1):67-77. doi: 10.1007/s42770-018-0035-0. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Braz J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30637647 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and immunological characterization of three potential vaccinogens against Cryptosporidium species.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011 Nov;18(11):1796-802. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05197-11. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21918117 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches to treatment of emerging Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections highlighting the O104:H4 serotype.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Mar 18;5:24. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00024. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25853096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Strategies for Infections With Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 6;10:169. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00169. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32435624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783-801. - PubMed
-
- Babiuk, S., D. J. Asper, D. Rogan, G. K. Mutwiri, and A. A. Potter. 2008. Subcutaneous and intranasal immunization with type III secreted proteins can prevent colonization and shedding of Escherichia coli in mice. Microb. Pathog. 45:7-11. - PubMed
-
- Bargieri, D. Y., D. S. Rosa, C. J. M. Braga, B. O. Carvalho, F. T. Costa, N. M. Spíndola, A. J. Vaz, I. S. Soares, L. C. S. Ferreira, and M. M. Rodrigues. 2008. New malaria vaccine candidates based on the Plasmodium vivax Merozoite Surface Protein-1 and the TLR-5 agonist Salmonella Typhimurium FliC flagellin. Vaccine 26:6132-6142. - PubMed
-
- Bentancor, L. V., M. Bilen, R. J. Fernández Brando, M. V. Ramos, L. C. S. Ferreira, P. D. Ghiringhelli, and M. S. Palermo. 2009. DNA vaccine encoding the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) Shiga-like toxin 2 (Stx2) A2 and B subunits confers protective immunity to Stx challenge in the murine model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 16:712-718. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

