The guanine exchange factor vav controls axon growth and guidance during Drosophila development
- PMID: 20147552
- PMCID: PMC6634040
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1820-09.2010
The guanine exchange factor vav controls axon growth and guidance during Drosophila development
Abstract
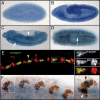
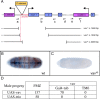
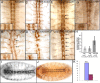
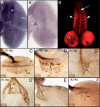
The Vav proteins are guanine exchange factors (GEFs) that trigger the activation of the Rho GTPases in general and the Rac family in particular. While the role of the mammalian vav genes has been extensively studied in the hematopoietic system and the immune response, there is little information regarding the role of vav outside of these systems. Here, we report that the single Drosophila vav homolog is ubiquitously expressed during development, although it is enriched along the embryonic ventral midline and in the larval eye discs and brain. We have analyzed the role that vav plays during development by generating Drosophila null mutant alleles. Our results indicate that vav is required during embryogenesis to prevent longitudinal axons from crossing the midline. Later on, during larval development, vav is required within the axons to regulate photoreceptor axon targeting to the optic lobe. Finally, we demonstrate that adult vav mutant escapers, which exhibit coordination problems, display axon growth defects in the ellipsoid body, a brain area associated with locomotion control. In addition, we show that vav interacts with other GEFs known to act downstream of guidance receptors. Thus, we propose that vav acts in coordination with other GEFs to regulate axon growth and guidance during development by linking guidance signals to the cytoskeleton via the modulation of Rac activity.
Figures



References
-
- Awasaki T, Saito M, Sone M, Suzuki E, Sakai R, Ito K, Hama C. The Drosophila trio plays an essential role in patterning of axons by regulating their directional extension. Neuron. 2000;26:119–131. - PubMed
-
- Bateman J, Shu H, Van Vactor D. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor trio mediates axonal development in the Drosophila embryo. Neuron. 2000;26:93–106. - PubMed
-
- Betz R, Sandhoff K, Fischer KD, van Echten-Deckert G. Detection and identification of Vav1 protein in primary cultured murine cerebellar neurons and in neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y and Neuro-2a) Neurosci Lett. 2003;339:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Boquet I, Hitier R, Dumas M, Chaminade M, Préat T. Central brain postembryonic development in Drosophila: implication of genes expressed at the interhemispheric junction. J Neurobiol. 2000a;42:33–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
