Hypocretins regulate the anxiogenic-like effects of nicotine and induce reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior
- PMID: 20147556
- PMCID: PMC2829191
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5724-09.2010
Hypocretins regulate the anxiogenic-like effects of nicotine and induce reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior
Abstract
Emerging evidence suggests that the hypocretinergic system is involved in addictive behavior. In this study, we investigated the role of these hypothalamic neuropeptides in anxiety-like responses of nicotine and stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior. Acute nicotine (0.8 mg/kg, s.c.) induced anxiogenic-like effects in the elevated plus-maze and activated the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) as revealed by c-Fos expression. Pretreatment with the hypocretin receptor 1 (Hcrtr-1) antagonist SB334867 or preprohypocretin gene deletion blocked both nicotine effects. In the PVN, SB334867 also prevented the activation of corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) and arginine-vasopressin (AVP) neurons, which expressed Hcrtr-1. In addition, an increase of the percentage of c-Fos-positive hypocretin cells in the perifornical and dorsomedial hypothalamic (PFA/DMH) areas was found after nicotine (0.8 mg/kg, s.c.) administration. Intracerebroventricular infusion of hypocretin-1 (Hcrt-1) (0.75 nmol/1 mul) or footshock stress reinstated a previously extinguished nicotine-seeking behavior. The effects of Hcrt-1 were blocked by SB334867, but not by the CRF1 receptor antagonist antalarmin. Moreover, SB334867 did not block CRF-dependent footshock-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking while antalarmin was effective in preventing this nicotine motivational response. Therefore, the Hcrt system interacts with CRF and AVP neurons in the PVN and modulates the anxiogenic-like effects of nicotine whereas Hcrt and CRF play a different role in the reinstatement of nicotine-seeking. Indeed, Hcrt-1 reinstates nicotine-seeking through a mechanism independent of CRF activation whereas CRF mediates the reinstatement induced by stress.
Figures
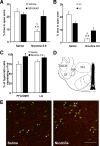
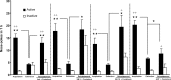
 p < 0.05 compared with KO or SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). D, Schematic anatomic representation of LH subdivisions adapted from Paxinos and Franklin's stereotaxic atlas (Paxinos and Franklin, 1997). Labeled areas delineate regions where c-Fos expression was examined. E, Representative images of sections of the PFA/DMH obtained via confocal microscopy after direct double labeling combining rabbit polyclonal antiserum to c-Fos with mouse monoclonal antibody to Hcrt-1. Arrowheads indicate c-Fos-positive Hcrt-1-expressing neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm.
p < 0.05 compared with KO or SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). D, Schematic anatomic representation of LH subdivisions adapted from Paxinos and Franklin's stereotaxic atlas (Paxinos and Franklin, 1997). Labeled areas delineate regions where c-Fos expression was examined. E, Representative images of sections of the PFA/DMH obtained via confocal microscopy after direct double labeling combining rabbit polyclonal antiserum to c-Fos with mouse monoclonal antibody to Hcrt-1. Arrowheads indicate c-Fos-positive Hcrt-1-expressing neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm.

 p < 0.01 compared with KO or SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). C, D, Representative images of the PVN obtained by microscopy after direct-labeling with rabbit polyclonal antiserum to c-Fos. Scale bar, 100 μm.
p < 0.01 compared with KO or SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). C, D, Representative images of the PVN obtained by microscopy after direct-labeling with rabbit polyclonal antiserum to c-Fos. Scale bar, 100 μm.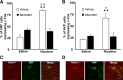
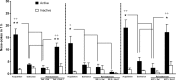
 p < 0.05,
p < 0.05, 
 p < 0.01 compared with SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). Representative images of sections of the PVN are shown in supplemental Figure 5 (available at
p < 0.01 compared with SB334867-pretreated nicotine-treated mice (one-way ANOVA). Representative images of sections of the PVN are shown in supplemental Figure 5 (available at 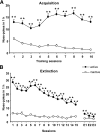
Similar articles
-
Hypocretin/orexin signaling in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus is essential for the expression of nicotine withdrawal.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Feb 1;71(3):214-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.06.025. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 21831361
-
Reinstatement of cocaine seeking by hypocretin (orexin) in the ventral tegmental area: independence from the local corticotropin-releasing factor network.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 May 15;65(10):857-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19251246 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine self-administration in the rat: effects of hypocretin antagonists and changes in hypocretin mRNA.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Apr;209(2):203-12. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1792-0. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20177882 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and arousal: the corticotrophin-releasing factor/hypocretin circuitry.Mol Neurobiol. 2005 Dec;32(3):285-94. doi: 10.1385/MN:32:3:285. Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16385142 Review.
-
Neuropeptide systems and new treatments for nicotine addiction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 May;234(9-10):1419-1437. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4513-5. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28028605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of δ-opioid receptors in the behavioral effects of nicotine.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Sep;37(10):2332-44. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.88. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22669166 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of lateral hypothalamic group III metabotropic glutamate receptors suppresses cocaine-seeking following abstinence and normalizes drug-associated increases in excitatory drive to orexin/hypocretin cells.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Aug;154:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.09.033. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30253175 Free PMC article.
-
Anxiety, depression and methods of stress coping in patients with nicotine dependence syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2011 May;17(5):CR272-6. doi: 10.12659/msm.881767. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 21525809 Free PMC article.
-
The Orexin/Receptor System: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential for Neurological Diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jun 28;11:220. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00220. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30002617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the orexin/hypocretin system in the pharmacological effects induced by Δ(9) -tetrahydrocannabinol.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;173(8):1381-92. doi: 10.1111/bph.13440. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26799708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bäckberg M, Hervieu G, Wilson S, Meister B. Orexin receptor-1 (OX-R1) immunoreactivity in chemically identified neurons of the hypothalamus: focus on orexin targets involved in control of food and water intake. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15:315–328. - PubMed
-
- Balerio GN, Aso E, Berrendero F, Murtra P, Maldonado R. Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol decreases somatic and motivational manifestations of nicotine withdrawal in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:2737–2748. - PubMed
-
- Balerio GN, Aso E, Maldonado R. Involvement of the opioid system in the effects induced by nicotine on anxiety-like behaviour in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;181:260–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
