Mechanisms underlying lateral GABAergic feedback onto rod bipolar cells in rat retina
- PMID: 20147559
- PMCID: PMC2836865
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5574-09.2010
Mechanisms underlying lateral GABAergic feedback onto rod bipolar cells in rat retina
Abstract
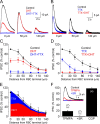
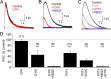
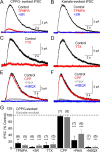
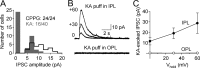
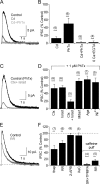
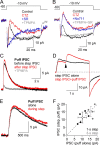
GABAergic feedback inhibition from amacrine cells shapes visual signaling in the inner retina. Rod bipolar cells (RBCs), ON-sensitive cells that depolarize in response to light increments, receive reciprocal GABAergic feedback from A17 amacrine cells and additional GABAergic inputs from other amacrine cells located laterally in the inner plexiform layer. The circuitry and synaptic mechanisms underlying lateral GABAergic inhibition of RBCs are poorly understood. A-type and rho-subunit-containing (C-type) GABA receptors (GABA(A)Rs and GABA(C)Rs) mediate both forms of inhibition, but their relative activation during synaptic transmission is unclear, and potential interactions between adjacent reciprocal and lateral synapses have not been explored. Here, we recorded from RBCs in acute slices of rat retina and isolated lateral GABAergic inhibition by pharmacologically ablating A17 amacrine cells. We found that amacrine cells providing lateral GABAergic inhibition to RBCs receive excitatory synaptic input mostly from ON bipolar cells via activation of both Ca(2+)-impermeable and Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors (CP-AMPARs) but not NMDA receptors (NMDARs). Voltage-gated Ca(2+) (Ca(v)) channels mediate the majority of Ca(2+) influx that triggers GABA release, although CP-AMPARs contribute a small component. The intracellular Ca(2+) signal contributing to transmitter release is amplified by Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores via activation of ryanodine receptors. Furthermore, lateral nonreciprocal feedback is mediated primarily by GABA(C)Rs that are activated independently from receptors mediating reciprocal feedback inhibition. These results illustrate numerous physiological differences that distinguish GABA release at reciprocal and lateral synapses, indicating complex, pathway-specific modulation of RBC signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Bloomfield SA. Relationship between receptive and dendritic field size of amacrine cells in the rabbit retina. J Neurophysiol. 1992;68:711–725. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA, Völgyi B. Response properties of a unique subtype of wide-field amacrine cell in the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci. 2007;24:459–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
