A subpopulation of neuronal M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors plays a critical role in modulating dopamine-dependent behaviors
- PMID: 20147565
- PMCID: PMC2824442
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3843-09.2010
A subpopulation of neuronal M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors plays a critical role in modulating dopamine-dependent behaviors
Abstract
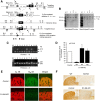
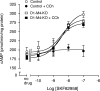
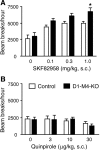
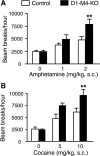
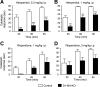
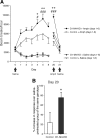
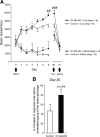
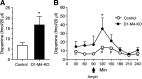
Acetylcholine (ACh) regulates many key functions of the CNS by activating cell surface receptors referred to as muscarinic ACh receptors (M(1)-M(5) mAChRs). Like other mAChR subtypes, the M(4) mAChR is widely expressed in different regions of the forebrain. Interestingly, M(4) mAChRs are coexpressed with D(1) dopamine receptors in a specific subset of striatal projection neurons. To investigate the physiological relevance of this M(4) mAChR subpopulation in modulating dopamine-dependent behaviors, we used Cre/loxP technology to generate mutant mice that lack M(4) mAChRs only in D(1) dopamine receptor-expressing cells. The newly generated mutant mice displayed several striking behavioral phenotypes, including enhanced hyperlocomotor activity and increased behavioral sensitization following treatment with psychostimulants. These behavioral changes were accompanied by a lack of muscarinic inhibition of D(1) dopamine receptor-mediated cAMP stimulation in the striatum and an increase in dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens. These novel findings demonstrate that a distinct subpopulation of neuronal M(4) mAChRs plays a critical role in modulating several important dopamine-dependent behaviors. Since enhanced central dopaminergic neurotransmission is a hallmark of several severe disorders of the CNS, including schizophrenia and drug addiction, our findings have substantial clinical relevance.
Figures
References
-
- Borgkvist A, Fisone G. Psychoactive drugs and regulation of the cAMP/PKA/DARPP-32 cascade in striatal medium spiny neurons. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2007;31:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Brady AE, Jones CK, Bridges TM, Kennedy JP, Thompson AD, Heiman JU, Breininger ML, Gentry PR, Yin H, Jadhav SB, Shirey JK, Conn PJ, Lindsley CW. Centrally active allosteric potentiators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reverse amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotor activity in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;327:941–953. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bymaster FP, Felder CC, Ahmed S, McKinzie D. Muscarinic receptors as a target for drugs treating schizophrenia. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2002;1:163–181. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A. The current status of the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1988;1:179–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
