Response of cardiac sympathetic nerve activity to intravenous irbesartan in heart failure
- PMID: 20147604
- PMCID: PMC2853391
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00767.2009
Response of cardiac sympathetic nerve activity to intravenous irbesartan in heart failure
Abstract
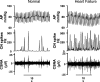
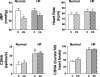
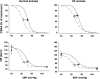
To determine the effect of irbesartan treatment on resting levels and arterial baroreflex control of cardiac sympathetic nerve activity (CSNA) in heart failure (HF), we studied conscious normal sheep and sheep with HF induced by rapid ventricular pacing for 8-10 wk (n = 7 per group). In HF, there is a large increase in CSNA that is detrimental to outcome. The causes of this increase in CSNA and the effect of angiotensin receptor blockers on CSNA in HF are unclear. CSNA, arterial blood pressure, heart rate (HR), and arterial baroreflex curves were recorded during a resting period and after 90 min of irbesartan infusion (12 mg.kg(-1).h(-1) iv). This dose of irbesartan abolished the pressor response to intravenous ANG II infusion but caused only a slight decrease in the pressor response to centrally administered ANG II. In HF, there was a large increase in CSNA (from 44 +/- 3 to 87 +/- 3 bursts/100 heartbeats). Irbesartan reduced arterial pressure in the normal and HF groups, but the usual baroreflex-mediated increases in CSNA and HR were prevented. This resulted from a significant leftward shift in the CSNA and HR baroreflex curves in both groups. Irbesartan also decreased the sensitivity of the arterial baroreflex control of CSNA. Short-term treatment with an angiotensin receptor blocker, at a dose that abolished the response to circulating, but not central, ANG II, prevented the reflex increase in CSNA in response to the drug-induced fall in arterial pressure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Central angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade decreases cardiac but not renal sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure.Hypertension. 2012 Mar;59(3):634-41. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.181131. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22311902 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endothelin-1 in mediating changes in cardiac sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;310(1):R94-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00205.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26468257
-
Central exogenous nitric oxide decreases cardiac sympathetic drive and improves baroreflex control of heart rate in ovine heart failure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;307(3):R271-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00057.2014. Epub 2014 May 21. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24848361
-
Cardiac sympathoexcitation in heart failure.Auton Neurosci. 2013 Apr;175(1-2):76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.10.017. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Auton Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23332860 Review.
-
Specific control of sympathetic nerve activity to the mammalian heart and kidney.Exp Physiol. 2010 Jan;95(1):34-40. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.046342. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Exp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19617268 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of angiotensin II signaling following exercise training in heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Apr 15;308(8):H781-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00026.2015. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25681422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sympathoactivation and rho-kinase-dependent baroreflex function in experimental renovascular hypertension with reduced kidney mass.BMC Physiol. 2014 Jun 19;14:4. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-14-4. BMC Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24946879 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-(1-7) in paraventricular nucleus modulates sympathetic activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in renovascular hypertensive rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048966. Epub 2012 Nov 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23139827 Free PMC article.
-
Central angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade decreases cardiac but not renal sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure.Hypertension. 2012 Mar;59(3):634-41. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.181131. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Hypertension. 2012. PMID: 22311902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- . Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS) The CONSENSUS Trial Study Group. N Engl J Med 316: 1429–1435, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Brunner-La Rocca HP, Esler MD, Jennings GL, Kaye DM. Effect of cardiac sympathetic nervous activity on mode of death in congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J 22: 1136–1143, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Brunner-La Rocca HP, Vaddadi G, Esler MD. Recent insight into therapy of congestive heart failure: focus on ACE inhibition and angiotensin-II antagonism. J Am Coll Cardiol 33: 1163–1173, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Culman J, von Heyer C, Piepenburg B, Rascher W, Unger T. Effects of systemic treatment with irbesartan and losartan on central responses to angiotensin II in conscious, normotensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 367: 255–265, 1999 - PubMed
-
- De Tommasi E, Iacoviello M, Romito R, Ceconi C, Guida P, Massari F, Francolini G, Bertocchi F, Ferrari R, Rizzon P, Pitzalis MV. Comparison of the effect of valsartan and lisinopril on autonomic nervous system activity in chronic heart failure. Am Heart J 146: E17, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

