Morphine peripheral analgesia depends on activation of the PI3Kgamma/AKT/nNOS/NO/KATP signaling pathway
- PMID: 20147620
- PMCID: PMC2840166
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914733107
Morphine peripheral analgesia depends on activation of the PI3Kgamma/AKT/nNOS/NO/KATP signaling pathway
Abstract
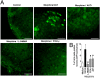
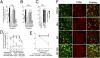
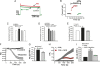
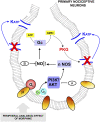
Morphine is one of the most prescribed and effective drugs used for the treatment of acute and chronic pain conditions. In addition to its central effects, morphine can also produce peripheral analgesia. However, the mechanisms underlying this peripheral action of morphine have not yet been fully elucidated. Here, we show that the peripheral antinociceptive effect of morphine is lost in neuronal nitric-oxide synthase null mice and that morphine induces the production of nitric oxide in primary nociceptive neurons. The activation of the nitric-oxide pathway by morphine was dependent on an initial stimulation of PI3Kgamma/AKT protein kinase B (AKT) and culminated in increased activation of K(ATP) channels. In the latter, this intracellular signaling pathway might cause a hyperpolarization of nociceptive neurons, and it is fundamental for the direct blockade of inflammatory pain by morphine. This understanding offers new targets for analgesic drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

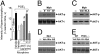
References
-
- Ferreira SH, Nakamura M. II—Prostaglandin hyperalgesia: The peripheral analgesic activity of morphine, enkephalins and opioid antagonists. Prostaglandins. 1979;18:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira SH, Nakamura M. I—Prostaglandin hyperalgesia, a cAMP/Ca2+ dependent process. Prostaglandins. 1979;18:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Collier HO, Roy AC. Morphine-like drugs inhibit the stimulation of E prostaglandins of cyclic AMP formation by rat brain homogenate. Nature. 1974;248:24–27. - PubMed
-
- Levine JD, Taiwo YO. Involvement of the mu-opiate receptor in peripheral analgesia. Neuroscience. 1989;32:571–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

