Adenosine deaminase modulation of telomerase activity and replicative senescence in human CD8 T lymphocytes
- PMID: 20147632
- PMCID: PMC3772624
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903647
Adenosine deaminase modulation of telomerase activity and replicative senescence in human CD8 T lymphocytes
Abstract
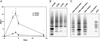
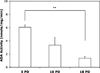
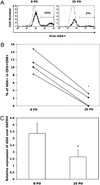
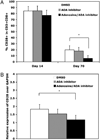
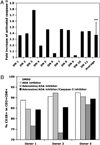
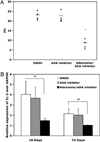
Increased proportions of CD8 T lymphocytes lacking expression of the CD28 costimulatory receptor have been documented during both aging and chronic infection with HIV-1, and their abundance correlates with numerous deleterious clinical outcomes. CD28-negative cells also arise in cell cultures of CD8(+)CD28(+) following multiple rounds of Ag-driven proliferation, reaching the end stage of replicative senescence. The present study investigates the role of a second T cell costimulatory receptor component, adenosine deaminase (ADA), on the process of replicative senescence. We had previously reported that CD28 signaling is required for optimal telomerase upregulation. In this study, we show that the CD8(+)CD28(+) T lymphocytes that are ADA(+) have significantly greater telomerase activity than those that do not express ADA and that ADA is progressively lost as cultures progress to senescence. Because ADA converts adenosine to inosine, cells lacking this enzyme might be subject to prolonged exposure to adenosine, which has immunosuppressive effects. Indeed, we show that chronic exposure of CD8 T lymphocytes to exogenous adenosine accelerates the process of replicative senescence, causing a reduction in overall proliferative potential, reduced telomerase activity, and blunted IL-2 gene transcription. The loss of CD28 expression was accelerated, in part due to adenosine-induced increases in constitutive caspase-3, known to act on the CD28 promoter. These findings provide the first evidence for a role of ADA in modulating the process of replicative senescence and suggest that strategies to enhance this enzyme may lead to novel therapeutic approaches for pathologies associated with increases in senescent CD8 T lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Valenzuela HF, Effros RB. Divergent telomerase and CD28 expression patterns in human CD4 and CD8 T cells following repeated encounters with the same antigenic stimulus. Clin. Immunol. 2002;105:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Lindstein T, June CH, Ledbetter JA, Stella G, Thompson CB. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989;244:339–43. - PubMed
-
- Powell JD, Ragheb JA, Kitagawa-Sakakida S, Schwartz RH. Molecular regulation of interleukin-2 expression by CD28 co-stimulation and anergy. Immunol. Rev. 1998;165:287–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

