Confirmation and generalization of an alcohol-dependence locus on chromosome 10q
- PMID: 20147890
- PMCID: PMC2855759
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2010.1
Confirmation and generalization of an alcohol-dependence locus on chromosome 10q
Abstract
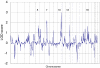
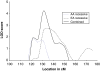
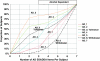
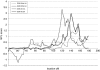
Several genome scans on alcohol dependence (AD) and AD-related traits have been published. In this article, we present the results of a genome-wide linkage scan on AD and several related traits in 322 European-American (EA) families, and results of additional analysis in 335 African-American (AA) families that were the subject of a previous report. All families were initially ascertained for cocaine and/or opioid dependence. Non-parametric linkage analysis in the EA sample revealed suggestive linkages on chromosomes 7 (LOD=2.1 at 82.8 cM, p=0.0009) and 10 (LOD=3.0 at 137.7 cM, p=0.0001). The chromosome 10 linkage peak is 20 cM distal from a genome-wide significant linkage peak we observed previously in the AA sample. Parametric linkage analysis on chromosome 10 (assuming a recessive model, 80% penetrance, disease allele frequency=0.3) resulted in LOD scores of 2.7 at 136.7 cM and 1.9 at 121.7 cM in the EA and AA samples, respectively, with a combined sample genome-wide significant LOD score of 4.1 at 131.7 cM. To reduce heterogeneity of the AD phenotype, we also assessed linkage of chromosome 10 markers with the presence of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, one of the seven components of the DSM-IV diagnosis of AD. Suggestive evidence for linkage was observed in both populations with only 5 cM separating the location of the peak LOD scores despite a loss of power due to a smaller number of families informative for this trait. Results of our study confirm a chromosome 10 risk locus for AD in two genetically distinct populations and suggest that this locus may correspond more precisely to a specific component of the disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autosomal linkage scan for loci predisposing to comorbid dependence on multiple substances.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012 Jun;159B(4):361-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32037. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012. PMID: 22354695 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific linkage scans in opioid dependence.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Apr;174(3):261-268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32507. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27762075 Free PMC article.
-
Dense genomewide linkage scan for alcohol dependence in African Americans: significant linkage on chromosome 10.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Jan 15;65(2):111-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.08.036. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 18930185 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide linkage scan of 409 European-ancestry and African American families with schizophrenia: suggestive evidence of linkage at 8p23.3-p21.2 and 11p13.1-q14.1 in the combined sample.Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Feb;78(2):315-33. doi: 10.1086/500272. Epub 2006 Jan 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16400611 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic approaches to addiction: genes and alcohol.Addiction. 2008 Sep;103(9):1414-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2008.02203.x. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Addiction. 2008. PMID: 18422824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A quantitative-trait genome-wide association study of alcoholism risk in the community: findings and implications.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Sep 15;70(6):513-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.028. Epub 2011 May 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21529783 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage analysis followed by association show NRG1 associated with cannabis dependence in African Americans.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Oct 15;72(8):637-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.02.038. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22520967 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal linkage scan for loci predisposing to comorbid dependence on multiple substances.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012 Jun;159B(4):361-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32037. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012. PMID: 22354695 Free PMC article.
-
Ordered subset linkage analysis based on admixture proportion identifies new linkage evidence for alcohol dependence in African-Americans.Hum Genet. 2013 Apr;132(4):397-403. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1255-2. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23239122 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Shared additive genetic influences on DSM-IV criteria for alcohol dependence in subjects of European ancestry.Addiction. 2015 Dec;110(12):1922-31. doi: 10.1111/add.13070. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Addiction. 2015. PMID: 26211938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders4th edn. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24DA15105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA015105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA022288/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HG-6540/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AA013736/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24AA013736/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

