Hypomania: a transcultural perspective
- PMID: 20148160
- PMCID: PMC2816932
- DOI: 10.1002/j.2051-5545.2010.tb00268.x
Hypomania: a transcultural perspective
Abstract
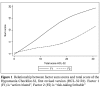
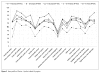
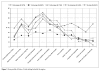
This study examined the transcultural robustness of a screening instrument for hypomania, the Hypomania Checklist-32, first revised version (HCL-32 R1). It was carried out in 2606 patients from twelve countries in five geographic regions (Northern, Southern and Eastern Europe, South America and East Asia). In addition, GAMIAN Europe contributed data from its members. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were used to examine the transregional stability of the measurement properties of the HCL-32 R1, including the influence of sex and age as covariates. Across cultures, a two-factor structure was confirmed: the first factor (F1) reflected the more positive aspects of hypomania (being more active, elated, self-confident, and cogni-tively enhanced); the second factor (F2) reflected the more negative aspects (being irritable, impulsive, careless, more substance use). The measurement properties of the HCL-32 R1 were largely invariant across cultures. Only few items showed transcultural differences in their relation to hypomania as measured by the test. F2 was higher among men and in more severe manic syndromes; F1 was highest in North and East Europe and lowest in South America. The scores decreased slightly with age. The frequency of the 32 items showed remarkable similarities across geographic areas, with two excep-tions: South Europeans had lower symptom frequencies in general and East Europeans higher rates of substance use. These findings support the interna-tional applicability of the HCL-32 R1 as a screening instrument for hypomania.
Keywords: HCL-32 R1,; Hypomania,; transcultural robustness.
Similar articles
-
Transcultural validity of the Hypomania Checklist-32 (HCL-32) in patients with major depressive episodes.Bipolar Disord. 2013 Sep;15(6):701-12. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12101. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Bipolar Disord. 2013. PMID: 23848428
-
Factor structure and reliability of the Italian adaptation of the Hypomania Check List-32, second revision (HCL-32-R2).J Affect Disord. 2015 Jun 1;178:112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 10. J Affect Disord. 2015. PMID: 25805403
-
Exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analysis of the korean version of hypomania checklist-32.Psychiatry Investig. 2011 Dec;8(4):334-9. doi: 10.4306/pi.2011.8.4.334. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Psychiatry Investig. 2011. PMID: 22216043 Free PMC article.
-
Cross validation with the mood disorder questionnaire (MDQ) of an instrument for the detection of hypomania in Brazil: The 32 item hypomania symptom check-list, first Revision (HCI-32-R1).J Affect Disord. 2012 Nov;140(3):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.12.033. Epub 2012 Jan 28. J Affect Disord. 2012. PMID: 22284020 Review.
-
Short versions of the 32-item Hypomania Checklist: A systematic review.Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2020 Jan;56(1):102-111. doi: 10.1111/ppc.12388. Epub 2019 May 8. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2020. PMID: 31066059
Cited by
-
Psychometric Properties of the Hypomania Checklist-32 in Korean Patients with Mood Disorders.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2017 Nov 30;15(4):352-360. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2017.15.4.352. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29073747 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomania-Checklist-33: risk stratification and factor structure in a mixed psychiatric adolescent sample.Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024 Aug 7;12(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40345-024-00350-x. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2024. PMID: 39112720 Free PMC article.
-
The new impact factor and immediacy index of World Psychiatry.World Psychiatry. 2012 Oct;11(3):207-8. doi: 10.1002/j.2051-5545.2012.tb00137.x. World Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23024687 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Symptom continuum reported by affective disorder patients through a structure-validated questionnaire.BMC Psychiatry. 2020 May 7;20(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02631-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32380965 Free PMC article.
-
Factorial structure and familial aggregation of the Hypomania Checklist-32 (HCL-32): Results of the NIMH Family Study of Affective Spectrum Disorders.Compr Psychiatry. 2018 Jul;84:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Compr Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29655654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jablensky A, Sartorius N, Ernberg E. A World Health Organization ten-country study. Psychol Med, Monograph. Suppl. 20. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992. Schizophrenia: manifestations, incidence and course in different cultures. - PubMed
-
- Piccinelli M, Gomez Homen F. Gender differences in the epidemiology of affective disorders and schizophrenia. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1997.
-
- Bruchmüller K, Meyer TD. Diagnostically irrelevant information can affect the likelihood of a diagnosis of bipolar disor-der. J Affect Disord. 2009;116:148–151. - PubMed
-
- Meyer F, Meyer TD. The misdiagnosis of bipolar disorder as a psychotic disorder: some of its causes and their influence on therapy. J Affect Disord. 2008;112:174–183. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous