EXCLUSION LEARNING AND EMERGENT SYMBOLIC CATEGORY FORMATION IN INDIVIDUALS WITH SEVERE LANGUAGE IMPAIRMENTS AND INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES
- PMID: 20148195
- PMCID: PMC2818096
- DOI: 10.1007/BF03395658
EXCLUSION LEARNING AND EMERGENT SYMBOLIC CATEGORY FORMATION IN INDIVIDUALS WITH SEVERE LANGUAGE IMPAIRMENTS AND INTELLECTUAL DISABILITIES
Abstract
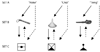
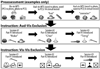
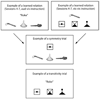
We evaluated formation of simple symbolic categories from initial learning of specific dictated word-picture relations through emergence of untaught or derived relations. Participants were 10 individuals with severe intellectual and language limitations. Three experimental categories were constructed, each containing 1 spoken word (Set A), 1 photograph (Set B), and 1 visual-graphic "lexigram" (Set C). Exclusion-based learning procedures were used to teach first the 3 auditory-visual relations (A-B relations) and then the 3 visual-visual relations (B-C relations) for each category. Seven participants acquired these initial relations. The untaught relations C-B and A-C were then assessed to evaluate the emergence of symbolic categories. Participants demonstrated virtually error-free performances on C-B and A-C derived relations. The study helps to define operationally a highly useful procedural path for systematic instruction in symbolic functioning for persons with intellectual and language disabilities associated with autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Brown L, Sherbenou RJ, Johnson SK. Test of nonverbal intelligence. 3rd ed. Austin, TX: PRO-ED; 1997.
-
- Carey S, Bartlett E. Acquiring a single new word. Papers and Reports on Child Language Development. 1978;15:17–29.
-
- Carr D, Felce J. Teaching picture-to-object relations in picture-based requesting by children with autism: A comparison between error prevention and error correction teaching procedures. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2008;52:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Chapman RS, Kay-raining Bird E, Schwartz SE. Fast mapping of words in event contexts by children with Down syndrome. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders. 1990;55:761–770. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
