Label-free biomarker sensing in undiluted serum with suspended microchannel resonators
- PMID: 20148583
- PMCID: PMC2847511
- DOI: 10.1021/ac9027356
Label-free biomarker sensing in undiluted serum with suspended microchannel resonators
Abstract
Improved methods are needed for routine, inexpensive monitoring of biomarkers that could facilitate earlier detection and characterization of cancer. Suspended microchannel resonators (SMRs) are highly sensitive, batch-fabricated microcantilevers with embedded microchannels that can directly quantify adsorbed mass via changes in resonant frequency. As in other label-free detection methods, biomolecular measurements in complex media such as serum are challenging due to high background signals from nonspecific binding. In this report, we demonstrate that carboxybetaine-derived polymers developed to adsorb directly onto SMR SiO(2) surfaces act as ultralow fouling and functionalizable surface coatings. Coupled with a reference microcantilever, this approach enables detection of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), a model cancer biomarker, in undiluted serum with a limit of detection of 10 ng/mL.
Figures
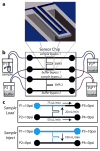




References
-
- Hanash SM, Pitteri SJ, Faca VM. Nature. 2008;452:571–579. - PubMed
-
- Sano T, Smith C, Cantor C. Science. 1992;258:120–122. - PubMed
-
- Fredriksson S, Gullberg M, Jarvius J, Olsson C, Pietras K, Gustafsdottir SM, Ostman A, Landegren U. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:473–477. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Snyder M. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

