Taurine protects against lung damage following limb ischemia reperfusion in the rat by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 20148646
- PMCID: PMC2895349
- DOI: 10.3109/17453671003587085
Taurine protects against lung damage following limb ischemia reperfusion in the rat by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis
Erratum in
- Acta Orthop. 2010 Oct;80(5):647
Abstract
Background and purpose: CHOP is a C/EBP family transcription factor involved in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis. Several studies have demonstrated that ischemia reperfusion results in apoptosis. Oxidative stress is central to ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis. Taurine protects against lung injury after limb ischemia reperfusion (LIR) through antioxidation. The effects of taurine on ER stress-induced apoptosis have not been well explored, however. We studied the effects of taurine in ER stress-induced apoptosis following LIR.
Methods: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 40) were randomized into 4 groups: (1) a control group, (2) an LIR group, (3) an LIR group treated with taurine, and (4) an LIR group treated with saline. Bilateral hindlimb ischemia was induced by application of a rubber band proximal to the level of the greater trochanters for 4 h. The treatment groups received either taurine (200 mg/kg as a 4% solution in 0.9% saline) or saline alone prior to reperfusion. Following 4h of reperfusion, blood oxygen was analyzed. The animals were killed and plasma and lung tissue were harvested for evaluation.
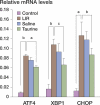
Results: Taurine statistically significantly attenuated lung injury following LIR, as shown by reduced malondialdehyde content, reduced cell apoptosis, and expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), and transcriptional activators of the CHOP gene. Furthermore, partial pressure values of oxygen in arterial blood and the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase were higher in the taurine pretreatment group than in the group of rats that underwent LIR alone.
Interpretation: Our results suggest that taurine attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in the lungs of rats after limb ischemia reperfusion.
Figures



References
-
- Benavides A, Pastor D, Santos P, Tranque P, Calvo S. CHOP plays a pivotal role in the astrocyte death induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation. Glia. 2005;52:261–75. - PubMed
-
- Beutler E. 1975:261–5. Red cell metabolism, Ed. 2. New York: Grune and Stratton Co.
-
- DeGracia DJ, Montie HL. Cerebral ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem. 2004;91:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978;201:875–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
