Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain
- PMID: 20148699
- PMCID: PMC2827151
- DOI: 10.3109/09553000903419346
Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain
Abstract
Purpose: Pro-inflammatory environments in the brain have been implicated in the onset and progression of neurological disorders. In the present study, we investigate the hypothesis that brain irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in cytokine gene and protein expression.
Materials and methods: Four month old F344 x BN rats received either whole brain irradiation with a single dose of 10 Gy gamma-rays or sham-irradiation, and were maintained for 4, 8, and 24 h following irradiation. The mRNA and protein expression levels of pro-inflammatory mediators were analysed by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and immunofluorescence staining. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of irradiation-induced brain inflammation, effects of irradiation on the DNA-binding activity of pro-inflammatory transcription factors were also examined.
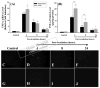
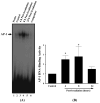
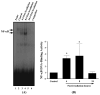
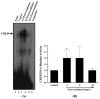
Results: A significant and marked up-regulation of mRNA and protein expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, including tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), was observed in hippocampal and cortical regions isolated from irradiated brain. Cytokine expression was regionally specific since TNF-alpha levels were significantly elevated in cortex compared to hippocampus (57% greater) and IL-1beta levels were elevated in hippocampus compared to cortical samples (126% greater). Increases in cytokine levels also were observed after irradiation of mouse BV-2 microglial cells. A series of electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) demonstrated that irradiation significantly increased activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1), nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB).
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that whole brain irradiation induces regionally specific pro-inflammatory environments through activation of AP-1, NF-kappaB, and CREB and overexpression of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and MCP-1 in rat brain and may contribute to unique pathways for the radiation-induced impairments in tissue function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
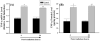
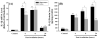
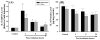
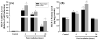
Similar articles
-
Relationship between irradiation-induced neuro-inflammatory environments and impaired cognitive function in the developing brain of mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2015 Mar;91(3):224-39. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2014.988895. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Int J Radiat Biol. 2015. PMID: 25426696
-
Role of NADPH oxidase in radiation-induced pro-oxidative and pro-inflammatory pathways in mouse brain.Int J Radiat Biol. 2017 Nov;93(11):1257-1266. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2017.1377360. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017. PMID: 28880721 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin inhibits expression of inducible NO synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured LPS-stimulated microglia via MAPK pathways.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021891. Epub 2011 Jul 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21765922 Free PMC article.
-
Aging attenuates radiation-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in rat brain.Neurosci Lett. 2010 May 31;476(2):89-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.04.009. Epub 2010 Apr 10. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20385203 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, sequential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and transcription factors precedes proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression in spleens of mice exposed to the trichothecene vomitoxin.Toxicol Sci. 2003 Mar;72(1):130-42. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfg006. Toxicol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12604842
Cited by
-
Radiotherapy induces an immediate inflammatory reaction in malignant glioma: a clinical microdialysis study.J Neurooncol. 2017 Jan;131(1):83-92. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2271-1. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 27664151 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation, inflammation and the immune response in cancer.Mamm Genome. 2018 Dec;29(11-12):843-865. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9777-0. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Mamm Genome. 2018. PMID: 30178305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Particle Radiation Induced Neurotoxicity in the Central Nervous System.Int J Part Ther. 2018 Summer;5(1):74-83. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-18-00026.1. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Part Ther. 2018. PMID: 31773021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short and Long-Term Toxicity in Pediatric Cancer Treatment: Central Nervous System Damage.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;14(6):1540. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061540. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole brain radiation-induced cognitive impairment: pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2012 Jul;20(4):357-70. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.20.4.357. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2012. PMID: 24009822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baluna RG, Eng TY, Thomas CR. Adhesion molecules in radiotherapy. Radiation Research. 2006;166:819–831. - PubMed
-
- Beetz A, Peter RU, Oppel T, Kaffenberger W, Rupec RA, Meyer M, van Beuningen D, Kind P, Messer G. NF-κB and AP-1 are responsible for inducibility of the IL-6 promoter by ionizing radiation in HeLa cells. International Journal of Radiation Biology. 2000;76:1443–1453. - PubMed
-
- Behrends U, Peter RU, Hintermeier-Knabe R, Eissner G, Holler E, Bornkamm GW, Caughman SW, Degitz K. Ionizing radiation induces human intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in vitro. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1994;103:726–730. - PubMed
-
- Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Bistoni F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. Journal of Neuroimmunology. 1990;27:229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
