The effect of image complexity on attentional bias towards alcohol-related images in adult drinkers
- PMID: 20148790
- PMCID: PMC2922935
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02860.x
The effect of image complexity on attentional bias towards alcohol-related images in adult drinkers
Abstract
Aim: Visual probe tasks are often used to measure attentional bias (AB) towards alcohol-related images in drinkers, but little is known about the effect of the properties of the images used in this task: specifically, image complexity.
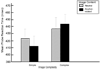
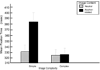
Methods: AB was examined in a group of adult drinkers (n = 25). Two measures of attentional bias were obtained from a modified visual probe task. First, a traditional dot probe detection task measured attentional bias in drinkers based on their reaction times to probes replacing neutral and alcohol-related images. Secondly, an eye-tracking measure was applied to this task to directly assess the drinkers' eye gazes to the alcohol-related and neutral images. The effect of image complexity was examined by comparing AB towards images classified as simple and complex.
Findings: Results showed that drinkers displayed AB only towards simple alcohol-related images as measured by both probe RT and fixation times.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that complex alcohol-related images might be less effective at capturing drinkers' attention and could result in less attentional bias when used in visual probe tasks.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Declaration:
The authors have no connection with the tobacco, alcohol, pharmaceutical or gaming industries or any body substantially funded by one of these organizations. There are no contractual constraints on publishing of this research.
Figures
References
-
- Robinson TE, Berridge KC. The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Rev. 1993;18:247–291. - PubMed
-
- Siegel S. Classical conditioning, drug tolerance, and drug dependence. In: Israel Y, Glaser F, Kalant H, Popham R, Schmidt W, Smart R, editors. Research Advances in Alcohol and Drug Problems. New York: Plenum; 1983. pp. 207–246.
-
- Duka T, Townshend JM. The priming effect of alcohol pre-load on attentional bias to alcohol-related stimuli. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004;176:353–362. - PubMed
-
- Field M, Mogg K, Bradley BP. Cognitive bias and drug craving in recreational cannabis users. Drug Alcohol Dep. 2004;74:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Townshend JM, Duka T. Attentional bias associated with alcohol cues: Differences between heavy and occasional social drinkers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;157:67–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

