CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) in human allergen-induced late nasal responses
- PMID: 20148806
- PMCID: PMC3380530
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02327.x
CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) in human allergen-induced late nasal responses
Abstract
Background: CC Chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) is preferentially expressed on Th2 lymphocytes. CCR4-mediated inflammation may be important in the pathology of allergic rhinitis. Disruption of CCR4 - ligand interaction may abrogate allergen-induced inflammation.
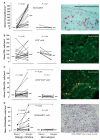
Methods: Sixteen allergic rhinitics and six nonatopic individuals underwent both allergen and control (diluent) nasal challenges. Symptom scores and peak nasal inspiratory flow were recorded. Nasal biopsies were taken at 8 h post challenge. Sections were immunostained and examined by light or dual immunofluorescence microscopy for eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, CCR4(+)CD3(+) and CXCR3(+)CD3(+) cells and examined by in situ hybridization for CCR4, IL-4 and IFN-gamma mRNA(+) cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were obtained from peripheral blood of nine normal donors and the CCR4(+)CD4(+) cells assessed for actin polymerization in response to the CCR4 ligand macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC/CCL22) and the influence of a CCR4 antagonist tested.
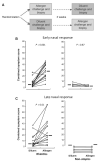
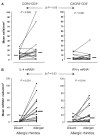
Results: Allergic rhinitics had increased early and late phase symptoms after allergen challenge compared to diluent; nonatopics did not respond to either challenge. Eosinophils, but not total numbers of CD3(+) T cells, were increased in rhinitics following allergen challenge. In rhinitics, there was an increase in CCR4(+)CD3(+) protein-positive cells relative to CXCR3(+)CD3(+) cells; CCR4 mRNA+ cells were increased and IL-4 increased to a greater extent than IFN-gamma. CCR4(+)CD4(+) T cells responded to MDC in vitro, and this response was inhibited by the selective CCR4 antagonist.
Conclusion: Lymphocyte CCR4 expression is closely associated with induction of human allergen-induced late nasal responses. Blocking CCR4-ligand interaction may provide a novel therapeutic approach in allergic disease.
Figures

References
-
- Cosmi L, Annunziato F, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Manetti R. Chemoattractant receptors expressed on type 2 T cells and their role in disease. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;125:273–279. - PubMed
-
- D’Ambrosio D, Iellem A, Bonecchi R, Mazzeo D, Sozzani S, Mantovani A, et al. Selective up-regulation of chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 upon activation of polarized human type 2 Th cells. J Immunol. 1998;161:5111–5115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

