A structural basis for the inhibition of collagen-stimulated platelet function by quercetin and structurally related flavonoids
- PMID: 20148891
- PMCID: PMC2848935
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00632.x
A structural basis for the inhibition of collagen-stimulated platelet function by quercetin and structurally related flavonoids
Abstract
Background and purpose: Molecular mechanisms underlying the links between dietary intake of flavonoids and reduced cardiovascular disease risk are only partially understood. Key events in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease, particularly thrombosis, are inhibited by these polyphenolic compounds via mechanisms such as inhibition of platelet activation and associated signal transduction, attenuation of generation of reactive oxygen species, enhancement of nitric oxide production and binding to thromboxane A(2) receptors. In vivo, effects of flavonoids are mediated by their metabolites, but the effects and modes of action of these compounds are not well-characterized. A good understanding of flavonoid structure-activity relationships with regard to platelet function is also lacking.
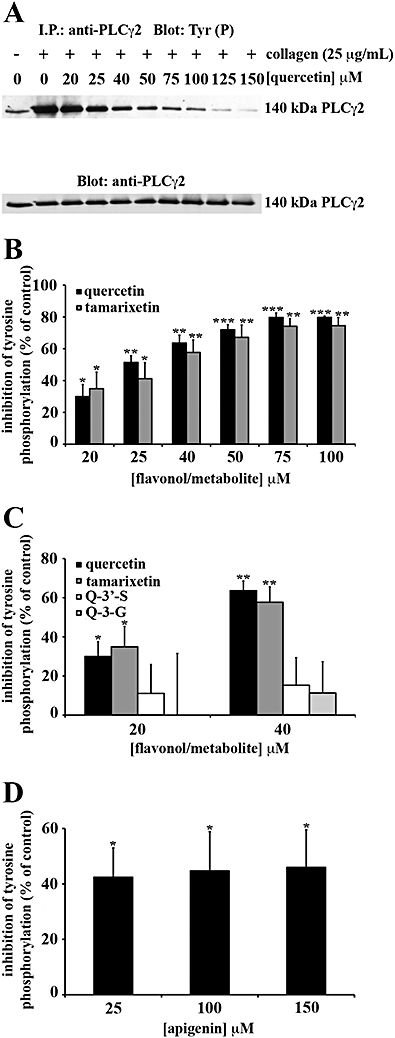
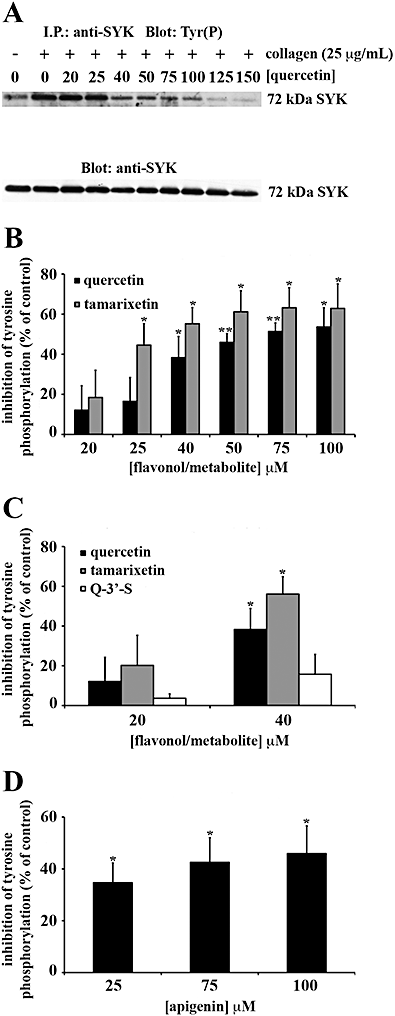
Experimental approach: Inhibitory potencies of structurally distinct flavonoids (quercetin, apigenin and catechin) and plasma metabolites (tamarixetin, quercetin-3'-sulphate and quercetin-3-glucuronide) for collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation and 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion were measured in human platelets. Tyrosine phosphorylation of total protein, Syk and PLCgamma2 (immunoprecipitation and Western blot analyses), and Fyn kinase activity were also measured in platelets. Internalization of flavonoids and metabolites in a megakaryocytic cell line (MEG-01 cells) was studied by fluorescence confocal microscopy.
Key results: The inhibitory mechanisms of these compounds included blocking Fyn kinase activity and the tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk and PLCgamma2 following internalization. Principal functional groups attributed to potent inhibition were a planar, C-4 carbonyl substituted and C-3 hydroxylated C ring in addition to a B ring catechol moiety.
Conclusions and implications: The structure-activity relationship for flavonoids on platelet function presented here may be exploited to design selective inhibitors of cell signalling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quercetin inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet activation through inhibition of multiple components of the glycoprotein VI signaling pathway.J Thromb Haemost. 2003 May;1(5):1079-88. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00212.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12871380
-
The toll-like receptor 2/1 (TLR2/1) complex initiates human platelet activation via the src/Syk/LAT/PLCγ2 signalling cascade.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):279-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.011. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24240055
-
Differential effects of quercetin, apigenin and genistein on signalling pathways of protease-activated receptors PAR(1) and PAR(4) in platelets.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;158(6):1548-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00440.x. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19814731 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role for the regulation of Syk from agglutination to aggregation in human platelets.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 10;443(2):580-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24326074
-
Insights into dietary flavonoids as molecular templates for the design of anti-platelet drugs.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jan 1;97(1):13-22. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs304. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23024269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Model yeast as a versatile tool to examine the antioxidant and anti-ageing potential of flavonoids, extracted from medicinal plants.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:980066. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.980066. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120300 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Polyphenols May Normalize Hypochlorous Acid-Evoked Hemostatic Abnormalities in Human Blood.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;11(4):779. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040779. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453464 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of specific functional groups in flavonoids on the modulation of platelet activation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 22;8(1):9528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27809-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29934595 Free PMC article.
-
A review of natural compounds to regulate platelet aggregation: molecular mechanism and research advance.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1537776. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1537776. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40657646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Anti-Prion Glyco-Based and Aromatic Scaffolds: A Chemical Strategy for the Quality of Life.Molecules. 2017 May 24;22(6):864. doi: 10.3390/molecules22060864. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28538692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agullo G, Gamet-Payrastre L, Manenti S, Viala C, Remesy C, Chap H, et al. Relationship between flavonoids structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:1649–1657. - PubMed
-
- Asselin J, Gibbins JM, Achison M, Lee YH, Morton LF, Farndale RW, et al. A collagen-like peptide stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of syk and phospholipase Cγ2 in platelets independent of the integrin α2β1. Blood. 1997;89:1235–1242. - PubMed
-
- Bell JRC, Donovan JL, Wong R, Waterhouse AL, German JB, Walzem RL, et al. (+)-catechin in human plasma after ingestion of a single serving of reconstituted red wine. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:103–108. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou M, Ryba NJ, Kihara H, Nishikata H, Siraganian RP. Protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk in high affinity IgE receptor signaling. Identification as a component of pp72 and association with the receptor gamma chain after receptor aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23318–23324. - PubMed
-
- Beretz A, Cazenave J-P, Anton R. Inhibition of aggregation and secretion of human platelets by quercetin and other flavonoids: structure-activity relationships. Agents Actions. 1982;12:382–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

